UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ý ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended: December 27, 2013
or
¨ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Commission File Number: 001-14543
____________________________________
TrueBlue, Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
______________________________________
|
| | |
Washington | | 91-1287341 |
(State of Incorporation) | | (IRS Employer ID) |
| |
1015 A Street, Tacoma, Washington | | 98402 |
(Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (253) 383-9101
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
| | |
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common Stock without par value | | The New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered under Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15 (d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Large accelerated filer ý Accelerated filer ¨ Non-accelerated filer ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) Smaller reporting company ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No ý
The aggregate market value (based on the NYSE quoted closing price) of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of the last business day of the second fiscal quarter, June 28, 2013, was approximately $0.834 billion.
As of February 3, 2014, there were 41,101,622 of the registrant’s common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The information required by Part III of this report is incorporated by reference from the registrant’s definitive proxy statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders scheduled to be held May 14, 2014, which definitive proxy statement will be filed no later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year to which this report relates.
COMMENT ON FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements. These statements relate to our expectations for future events and future financial performance. Generally, the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties, and future events and circumstances could differ significantly from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements. These statements are only predictions. Actual events or results may differ materially. Factors which could affect our financial results are described in Item 1A of this Form 10-K. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date hereof. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance, or achievements. Moreover, neither we nor any other person assume responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the forward-looking statements. We undertake no duty to update any of the forward-looking statements after the date of this report to conform such statements to actual results or to changes in our expectations.
TrueBlue, Inc.
2013 Annual Report on Form 10-K
Table of Contents
|
| | |
| | Page |
PART I |
Item 1. | | |
Item 1A. | | |
Item 1B. | | |
Item 2. | | |
Item 3. | | |
Item 4. | | |
PART II |
Item 5. | | |
Item 6. | | |
Item 7. | | |
Item 7A. | | |
Item 8. | | |
Item 9. | | |
Item 9A. | | |
Item 9B. | | |
PART III |
Item 10. | | |
Item 11. | | |
Item 12. | | |
Item 13. | | |
Item 14. | | |
PART IV |
Item 15. | | |
| | |
| | |
TrueBlue, Inc.
Form 10-K
PART I
TrueBlue, Inc. (“TrueBlue,” “we,” “us,” “our”) is a leading provider of temporary blue-collar staffing. We help over 130,000 businesses be more productive through easy access to dependable temporary labor. Through our Labor Ready, Spartan Staffing, CLP, PlaneTechs, and Centerline service lines, we connect approximately 375,000 people to work opportunities annually. We provide a wide range of specialized blue-collar staffing services to industries that include construction, manufacturing, transportation, aviation, waste, hospitality, retail, energy, and many more.
We operate as Labor Ready for general labor, Spartan Staffing for light industrial, CLP Resources for skilled trades, PlaneTechs for aviation and transportation mechanics and technicians, and Centerline Drivers for drivers. We have a network of 757 branches in all 50 states, Puerto Rico and Canada. We also have customer on-site locations, which are generally dedicated to one customer, and national service centers that supply our customers with temporary workers.
We began operations in 1989 under the name Labor Ready, Inc. providing on-demand, general labor staffing services. We became a public company in 1995. In 2004, we began acquiring additional staffing services to expand our service offerings to customers in the blue-collar staffing market. Effective December 18, 2007, Labor Ready, Inc. changed its name to TrueBlue, Inc. We are headquartered in Tacoma, Washington.
Temporary Staffing Industry
The temporary staffing industry supplies temporary staffing services to minimize the cost and effort of hiring and administering permanent employees, in order to rapidly respond to changes in business conditions, to temporarily replace absent employees, to temporarily fill new positions, and to convert fixed or permanent labor costs to variable or flexible costs. Temporary staffing companies act as intermediaries in matching available temporary workers to employer assignments. The demand for a flexible workforce continues to grow with competitive and economic pressures to reduce costs and respond to changing market conditions.
The temporary staffing industry is large and highly fragmented with many competing companies. No single company has a dominant share of the temporary staffing industry. Staffing companies compete both to recruit and retain a supply of temporary workers and to attract and retain customers to employ these workers. Customer demand for temporary staffing services is dependent on the overall strength of the labor market and workforce flexibility trends. The temporary staffing industry includes a number of markets focusing on business needs that vary widely in duration of assignment and level of skill and experience. We operate within the blue-collar staffing market of the temporary staffing industry.
The temporary staffing industry is subject to volatility based on overall economic conditions. Historically, in periods of economic growth, the number of companies providing temporary staffing services has increased due to low barriers to entry and during recessionary periods the number of companies has decreased through consolidation, bankruptcies, or other events. The temporary staffing industry is currently experiencing increased demand in relation to total job growth as customers have placed a greater priority on maintaining a more flexible workforce.
Business Strategy
Organic growth through specialized sales and service - Our customers have a variety of challenges in running their businesses, many of which are unique to the industry in which they operate. Our objective is to be the leading provider of blue-collar staffing by providing specialized service offerings that improve the productivity and performance of our customers. We believe our focus on the blue-collar staffing market and specialized knowledge of the industries in which our customers operate differentiates us from our competition. We plan to continue building the industry specialization of our sales and services teams while creating a more seamless experience for our customers to access all of our service lines. We also plan to increase our specialization by building additional expertise in sales, recruiting, and service by transitioning many of our generalist-oriented branch employee positions to dedicated position in one of these three key areas.
Growth through acquisitions which enhance our organic growth and technology advances - Strategic acquisitions continue to be a key growth strategy. We completed and fully integrated three acquisitions during fiscal 2013. We believe we have a core competence in assessing, valuing, and integrating acquisitions. We are excited about the future of the temporary staffing industry and believe we can continue to create shareholder value through acquisitions which expand our blue-collar service offerings, enhance our use of technology to better serve our customers, and increase our own efficiency.
Leveraging technology to improve the worker and customer experience and our efficiency - We continue to invest in technology which makes it easier for our customers and workers to do business with us. We completed the roll out of our mobile texting solution for all service lines in 2013. This has improved the experience of our temporary workers, reduced the amount of time it takes our branches to match and assign temporary workers, and expanded the geographic reach of our branches. We completed the roll out of our electronic pay solutions in 2012. Our workers are no longer required to come into the branch to be dispatched and again to be paid. This has improved the daily experience of our temporary workers as well as overall customer satisfaction.
We believe technology can increase the efficiency and quality of delivering our services. We believe we can further leverage technology to reduce the number of physical branches and centralize certain service functions. We intend to create more time for our field personnel to focus on high value sales and service activities by automating a variety of tasks. We believe centralizing certain service activities will create a more efficient delivery platform and the quality of these services for our customers.
Operations
We provide a wide range of specialized blue-collar staffing services. We operate as Labor Ready for on-demand general labor, Spartan Staffing for skilled manufacturing and logistics labor, CLP Resources for skilled trades for commercial, industrial and energy construction as well as building and plant maintenance, PlaneTechs for skilled mechanics and technicians to the aviation and transportation industries, and Centerline Drivers for temporary and dedicated drivers to the transportation and distribution industries. Our operations are all in the blue-collar staffing market of the temporary staffing industry. All our service lines:
| |
• | Provide blue-collar temporary labor services to our customers; |
| |
• | Serve customers who have a need for temporary staff to perform blue-collar tasks which do not require a permanent employee; |
| |
• | Build a temporary workforce through recruiting, screening and on-boarding. Temporary workers are dispatched to customers where they work under the supervision of our customers; |
| |
• | Drive profitability by managing the bill rates to our customers and the pay rates to our workers. Profitable growth requires increased volume, bill rates that grow faster than pay rates, and/or leveraging our cost structure; and |
| |
• | Use innovative technology to improve our ability to recruit quality workers, effectively match workers to the needs of our customers, and meet our customers' needs more efficiently. We are focused on improving the ease of doing business with us for both our temporary workers and customers. |
Our long-term financial performance expectations of all our service lines are similar as are the underlying financial and economic metrics used to manage those service lines. Profitable growth is driven by leveraging our cost structure across all service lines to achieve economies of scale and investing in technology that improves our productivity.
Our business is generally conducted through a broad network of local branch locations, customer on-site locations generally dedicated to one customer, and national service centers. We have a growing capability to service remote customer needs and work sites where we have no physical location. Management of our temporary staffing operations is coordinated from our headquarters in Tacoma, Washington where we provide centralized support services to our field operations.
Customers
Our customer mix consists primarily of small and medium-sized businesses serviced by one or more branch offices, customer on-site locations, and national service centers. We also serve larger regional and national customers. Our full range of blue-collar temporary staffing services enables us to meet all the blue-collar staffing needs of our customers.
Our sales process takes place at the customer’s location. Temporary staffing services to our customers vary depending on the local labor supply, the length of assignment, the number of workers, and the skills required. We are a business-to-business sales provider. Retention of customers, exclusive of economic conditions, is dependent on the strength of our relationship with the customer, the skill, quality and tenure of temporary workers, and customer service.
During 2013, we served approximately 130,000 customers in industries including construction, manufacturing, waste, wholesale, retail, transportation, aviation, hospitality, energy and many more. Our ten largest customers accounted for 16% of total revenue for 2013, 22% for 2012, and 19% for 2011. Sales to our largest customer accounted for 5% of total revenue for 2013, 7% for 2012, and 8% for 2011.
Employees and Temporary Workers
As of December 27, 2013, we employed approximately 3,200 full-time equivalent employees. In addition, we placed approximately 375,000 temporary workers on assignments with our customers during 2013. We recruit temporary workers daily so that we can be responsive to the planned as well as unplanned needs of the customers we serve. We attract our pool of temporary workers through personal referrals, online resources, extensive internal databases, advertising, job fairs, and various other methods. We identify the skills, knowledge, abilities, and personal characteristics of a temporary worker and match their competencies and capabilities to a customer’s requirements. This enables our customers to obtain immediate value by placing a highly productive employee on the job site. We use a variety of proprietary programs and methods for identifying and assessing the skill level of our temporary workers when selecting a particular individual for a specific assignment and retaining those workers for future assignments. We believe that our programs and methods enable us to offer a higher quality of service by increasing productivity, decreasing turnover, and reducing absenteeism.
We provide a bridge to permanent, full-time employment for thousands of temporary workers each year. Temporary workers also come to us to fill a short-term financial need. Many stay because of the flexibility that we offer. Temporary workers may be assigned to different jobs and job sites, and their assignments could last for as little as a few hours or extend for several weeks or months. We provide our temporary workers meaningful work and the opportunity to improve their skills. We are considered the legal employer of our temporary workers, and laws regulating the employment relationship are applicable to our operations. We consider our relations with our employees and temporary workers to be good.
Competition
We compete in the temporary staffing industry by offering a full range of blue-collar staffing services. The temporary staffing industry is large and fragmented, comprising thousands of companies employing millions of people, and generating billions of dollars in annual revenues.
We experience competition in attracting customers as well as qualified temporary workers. The staffing business is highly competitive with limited barriers to entry, resulting in numerous firms offering services similar to those provided by us on an international, national, regional, and/or local basis. We compete with several multi-national full-service and specialized temporary staffing companies, as well as many local companies. The majority of temporary staffing companies serving the blue-collar staffing market are locally-owned businesses. In most geographic areas, no single company has a dominant share of the market. In many areas the local companies are the strongest competitors, largely due to their longevity in the market and the strength of their customer relationships. We also experience competition from internet-based companies providing a variety of flexible workforce solutions. We expect this form of competition to grow in the future and require changes in the way we do business to remain relevant to our customers.
Competitive forces have historically limited our ability to raise our prices to immediately and fully offset increased costs of doing business, some of which include increased temporary worker wages, costs for workers’ compensation, and unemployment insurance.
The most significant competitive factors in the staffing business are price, ability to promptly fill customer orders, success in meeting customers’ expectations of temporary workers, and appropriately addressing customer service issues. We believe we derive a competitive advantage from our service history, commitment to the blue-collar staffing market, and our specialized approach in serving the industries of our customers. Our national presence, proprietary systems, investment in technology and specialized programs focused on worker safety, risk management, and legal and regulatory compliance are also key differentiators from many of our competitors.
Seasonality and Cyclical Nature of our Business
Our business experiences seasonal fluctuations. Our quarterly operating results are affected by the seasonality of our customers’ businesses. Demand for our staffing services is higher during the second and third quarters of the year and peaks in the third quarter. Demand is lower during the first and fourth quarters, in part due to limitations to outside work during the winter months. Our working capital requirements are primarily driven by temporary worker payroll and customer accounts receivable. Since receipts from customers lag payroll to temporary workers, working capital requirements increase substantially in periods of growth.
The staffing industry has historically been cyclical, often acting as an indicator of both economic downturns and upswings. Staffing customers tend to use temporary staffing to supplement their existing workforces and generally hire permanent workers when long-term demand is expected to increase. As a consequence, our revenues tend to increase quickly when the economy begins to grow and, conversely, our revenues also decrease quickly when the economy begins to weaken. While we have longer-term customer relationships, which are not directly dependent upon the economic cycle, these revenues are not significant enough to offset the impact of cyclical economic activity for our temporary staffing services.
Financial Information about Geographic Areas
The following table depicts our revenue earned from within the United States and from international operations for the past three fiscal years (in millions, except percentages).
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
United States (including Puerto Rico) | $ | 1,617.9 |
| | 96.9 | % | | $ | 1,341.5 |
| | 96.5 | % | | $ | 1,266.3 |
| | 96.2 | % |
International operations | 50.9 |
| | 3.1 | % | | 48.0 |
| | 3.5 | % | | 49.7 |
| | 3.8 | % |
Total revenue from services | $ | 1,668.8 |
| | 100.0 | % | | $ | 1,389.5 |
| | 100.0 | % | | $ | 1,316.0 |
| | 100.0 | % |
Our international operations are in Canada and are dependent on shared information and communications equipment housed and maintained in the United States. Net property and equipment located in international operations was less than 2% of total property and equipment in each of the last three fiscal years.
Available Information
Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, along with all other reports and amendments filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) are publicly available, free of charge, on our website at www.trueblue.com or at www.sec.gov as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports are filed with or furnished to the SEC. Our Corporate Governance Guidelines, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and Board Committee Charters are also posted to our website. The information on our website is not part of this or any other report we file with, or furnish to, the SEC.
Investing in our securities involves risk. The following risk factors and all other information set forth in this Annual Report on Form 10-K should be considered in evaluating our future prospects. In particular, keep these risk factors in mind when you read “forward-looking” statements elsewhere in this report. Forward-looking statements relate to our expectations for future events and time periods. Generally, the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties, and future events and circumstances could differ significantly from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements. If any of the events described below occurs, our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity, or access to the capital markets could be materially and adversely affected.
Our business is significantly affected by fluctuations in general economic conditions.
The demand for our blue-collar staffing services is highly dependent upon the state of the economy and upon the staffing needs of our customers. As economic activity slows, companies tend to reduce their use of temporary employees before terminating their employees. Significant declines in demand and corresponding revenues can result in expense de-leveraging, which would result in lower profit levels. Any variation in the economic condition or unemployment levels of the United States, Puerto Rico, or Canada or in the economic condition of any region or specific industry in which we have a significant presence may severely reduce the demand for our services and thereby significantly decrease our revenues and profits. Deterioration in economic conditions or the financial or credit markets could also have adverse impacts on our customers' ability to pay us for services we have already provided.
Our business is subject to extensive government regulation which could materially harm our business.
Our business is subject to extensive regulation. The cost to comply, and any inability to comply, with government regulation could materially harm our business. Our temporary services business entails employing individuals on a temporary basis and placing such individuals in customers' workplaces. Increased government regulation of the workplace or of the employer-employee relationship, or judicial or administrative proceedings related to such regulation, could materially harm our business.
The wage rates we pay to temporary workers are based on many factors, including applicable minimum wage requirements. Increases in the minimum wage in regions across the country, or nationally, will increase our costs. With these wages, we pay a number of government mandated payroll-related costs and expenses, including unemployment insurance taxes. Unemployment insurance taxes paid by employers typically increase during periods of increased levels of unemployment. If we are not able to increase the fees charged to customers to absorb any increased costs related to minimum wages or unemployment insurance our results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (collectively, the “Health Care Reform Laws”) include various health-related provisions to take effect through 2015, including requiring most individuals to have health insurance and establishing new regulations on health plans. Although the Health Care Reform Laws do not mandate that employers offer health insurance, beginning in 2015 tax penalties will be assessed on large employers who do not offer health insurance that meets certain affordability or benefit requirements. Unless modified by regulations or subsequent legislation, providing such additional health insurance benefits to our temporary workers, or the payment of tax penalties if such coverage is not provided, will increase our costs. If we are unable to raise the rates we charge our customers to cover these costs, such increases in costs could materially harm our business.
We may incur employment related and other claims that could materially harm our business.
We employ individuals on a temporary basis and place them in our customers' workplaces. We have minimal control over our customers' workplace environments. As the employer of record of our temporary workers, we incur a risk of liability for various workplace events, including claims for personal injury, wage and hour violations, discrimination, harassment, failure to protect confidential personal information and other liabilities arising from the actions of our customers and temporary workers. In addition, some or all of these claims may give rise to litigation including class action litigation. A material adverse impact on our financial statements could occur for the period in which the effect of an unfavorable final outcome becomes probable and can be reasonably estimated.
We maintain insurance with respect to many of such claims. We cannot be certain that our insurance will be available, or if available, in sufficient amount or scope to cover all claims that may be asserted against us. Should the ultimate judgments or settlements exceed our insurance coverage, they could have a material effect on our business. We cannot be certain we will be able to obtain appropriate types or levels of insurance in the future, that adequate replacement policies will be available on acceptable terms, or at all, or that the companies from which we have obtained insurance will be able to pay claims we make under such policies.
We are dependent on workers' compensation insurance coverage at commercially reasonable terms.
We provide workers' compensation insurance for our temporary workers. Our workers' compensation insurance policies are renewed annually. The majority of our insurance policies are with AIG. Our insurance carriers require us to collateralize a significant portion of our workers' compensation obligation. The majority of collateral is held in trust by a third party for the payment of these claims. The loss or decline in value of the collateral could require us to seek additional sources of capital to pay our workers' compensation claims. We cannot be certain we will be able to obtain appropriate types or levels of insurance in the future or that adequate replacement policies will be available on acceptable terms. As our business grows or if our financial results deteriorate, the amount of collateral required will likely increase and the timing of providing collateral could be accelerated. Resources to meet these requirements may not be available. The loss of our workers' compensation insurance coverage would prevent us from doing business in the majority of our markets. Further, we cannot be certain that our current and former insurance carriers will be able to pay claims we make under such policies.
Unexpected changes in claim trends on our worker's compensation may negatively impact our financial condition.
We self-insure, or otherwise bear financial responsibility for, a significant portion of expected losses under our workers' compensation program. Unexpected changes in claim trends, including the severity and frequency of claims, actuarial estimates and medical cost inflation, could result in costs that are significantly different than initially reported. There can be no assurance that we will be able to increase the fees charged to our customers in a timely manner and in a sufficient amount to cover increased costs as a result of any changes in claims-related liabilities.
We actively manage the safety of our temporary workers with our safety programs and actively control costs with our network of service providers. These activities have had a positive impact of reducing current and estimated future payouts as well as creating favorable adjustments to workers’ compensation liabilities recorded in prior periods. There can be no assurance that we will be able to continue to reduce accident rates and control costs to produce these results in the future.
Our liquidity may be materially adversely affected by constraints in the capital markets.
Our principal sources of liquidity are funds generated from operating activities, available cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, and borrowings under our credit facility. Certain of these investments are subject to general credit, liquidity, market, and interest rate risks and could materially decline in value. These risks may negatively impact our financial condition.
We must have sufficient sources of liquidity to meet our working capital requirements, fund our workers' compensation collateral requirements, service our outstanding indebtedness, and finance investment opportunities. Without sufficient liquidity, we could be forced to curtail our operations or we may not be able to pursue promising business opportunities.
Our failure to comply with the restrictive covenants under our revolving credit facility and/or term loan could result in an event of default, which, if not cured or waived, could result in our being required to repay these borrowings before their due date. If we are forced to refinance these borrowings on less favorable terms, or are unable to refinance at all, our results of operations and financial condition could be materially adversely affected by increased costs and rates.
Acquisitions and new business ventures may have an adverse effect on our business.
We expect to continue making acquisitions and entering into new business initiatives as part of our business strategy. This strategy may be impeded, however, if we cannot identify suitable acquisition candidates or new business initiatives, or if acquisition candidates are not available under terms that are acceptable to us. Future acquisitions could result in our incurring debt and contingent liabilities, an increase in interest expense, an increase in amortization expense, and/or significant charges related to integration costs. Acquisitions and new business initiatives involve significant challenges and risks, including that they may not advance our business strategy, we may not realize our anticipated return on our investment, we may experience difficulty in integrating operations, or management's attention may be diverted from our other business. These events could cause material harm to our business, operating results, or financial condition.
If our acquired intangible assets become impaired we may be required to record a significant charge to earnings.
We may not realize all the economic benefit from our acquisitions, which could result in future impairment of acquired intangibles. Under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States we review acquired intangible assets for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. We test goodwill and indefinite lived intangible assets for impairment at least annually. Factors that may be considered a change in circumstances, indicating that the carrying value of the intangible assets may not be recoverable, include a decline in stock price and market capitalization, reduced future cash flow estimates, and slower growth rates in our industry. We may be required to record a significant charge in our financial statements during the period in which we determine an impairment of our acquired intangible assets, negatively impacting our results of operations.
We operate in a highly competitive business and may be unable to retain customers or market share.
The staffing services business is highly competitive, rapidly innovating, and the barriers to entry are low. Large, well-financed competitors, as well as small new competitors, may increase pricing pressures. We also experience competition from internet-based companies providing a variety of flexible workforce solutions. We expect this form of competition to grow in the future and require innovation and changes in the way we do business to remain relevant to our customers. In addition, long-term contracts form only a small portion of our revenue. Therefore, there can be no assurance that we will be able to retain customers or market share in the future. Nor can there be any assurance that we will, in light of competitive pressures, be able to remain profitable or, if profitable, maintain our current profit margins.
Our management information systems are vulnerable to damage and interruption.
The efficient operation of our business is dependent on our management information systems. We rely heavily on proprietary management information systems to manage our order entry, order fulfillment, pricing, and collections, as well as temporary worker recruitment, dispatch, and payment. Our management information systems, mobile device technology and related services, and other technology may not yield the intended results. Our systems may experience problems with functionality and associated delays. The failure of our systems to perform as we anticipate could disrupt our business and could result in decreased revenue and increased overhead costs, causing our business and results of operations to suffer materially. Our primary computer systems and operations are vulnerable to damage or interruption from power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, security breaches, catastrophic events, and errors in usage by our employees. Failure of our systems to perform may require significant additional capital and management resources to resolve, causing material harm to our business.
Our results of operations could materially deteriorate if we fail to attract, develop and retain qualified employees.
Our performance is dependent on attracting and retaining qualified employees who are able to meet the needs of our customers. We believe our competitive advantage is providing unique solutions for each individual customer, which requires us to have highly trained and engaged employees. Our success depends upon our ability to attract, develop and retain a sufficient number of qualified employees, including management, sales, recruiting, service and administrative personnel. The turnover rate in the staffing industry is high, and qualified individuals of the requisite caliber and number needed to fill these positions may be in short supply. Our inability to recruit, train, and motivate a sufficient number of qualified individuals may delay or affect the speed of our planned growth or strategy change. Delayed expansion, significant increases in employee turnover rates or significant increases in labor costs could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may be unable to attract, manage, and retain sufficient qualified temporary workers.
We compete with other temporary staffing companies to meet our customer needs and we must continually attract qualified temporary workers to fill positions. Attracting and retaining skilled temporary employees depends on factors such as desirability of the assignment, location, and the associated wages and other benefits. We have in the past experienced worker shortages and we may experience such shortages in the future. Further, if there is a shortage of temporary workers, the cost to employ these individuals could increase. If we are unable to pass those costs through to our customers, it could materially and adversely affect our business. Organized labor periodically engages in efforts to represent various groups of our temporary workers. If we are subject to unreasonable collective bargaining agreements or work disruptions, our business could be adversely affected.
We may have additional tax liabilities that exceed our estimates.
We are subject to federal taxes and a multitude of state and local taxes in the United States and taxes in foreign jurisdictions. In the ordinary course of our business, there are transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax determination is uncertain. We are regularly subject to audit by tax authorities. Although we believe our tax estimates are reasonable, the final determination of tax audits and any related litigation could be materially different from our historical tax provisions and accruals. The results of an audit or litigation could materially harm our business.
Accidental disclosure of our employees' or customers' information could materially harm our business.
Failure to protect the integrity and security of our employees' and customers' information, including proprietary information, could expose us to litigation and materially damage our relationship with our employees and our customers. Further, data privacy is subject to frequently changing rules and regulations, which sometimes conflict among the various jurisdictions. Our failure to adhere to or successfully implement changes in response to the changing regulatory requirements could result in legal liability, additional compliance costs, and damage to our reputation.
Failure to maintain adequate financial and management processes and controls could lead to errors in our financial reporting.
If our management is unable to certify the effectiveness of our internal controls or if our independent registered public accounting firm cannot render an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, or if material weaknesses in our internal controls are identified, we could be subject to regulatory scrutiny and a loss of public confidence. In addition, if we do not maintain adequate financial and management personnel, processes and controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial performance on a timely basis, which could cause our stock price to fall.
Outsourcing certain aspects of our business could result in disruption and increased costs.
We have outsourced certain aspects of our business to third party vendors that subject us to risks, including disruptions in our business and increased costs. For example, we have engaged third parties to host and manage certain aspects of our data center, information and technology infrastructure, mobile texting and electronic pay solutions, and to provide certain back office support activities. Accordingly, we are subject to the risks associated with the vendor's ability to provide these services to meet our needs. If the cost of these services is more than expected, or if we or the vendor are unable to adequately protect our data and information is lost, or our ability to deliver our services is interrupted, then our business and results of operations may be negatively impacted.
| |
Item 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
We lease the building space at all our branch offices except for one that we own in Florida. Under the majority of these leases, both parties have the right to terminate the lease on 90 days notice. We own an office building in Tacoma, Washington, which serves as our headquarters. Management believes all our facilities are currently suitable for their intended use.
See discussion of legal contingencies and developments in Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| |
Item 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
None.
PART II.
| |
Item 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market Information
Our common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol TBI. The table below sets forth the high and low sales prices for our common stock as reported by the New York Stock Exchange during the last two fiscal years:
|
| | | | | |
| High | | Low |
2013 | | | |
Fourth Quarter | 27.43 |
| | 23.22 |
|
Third Quarter | 27.76 |
| | 20.35 |
|
Second Quarter | 23.82 |
| | 19.31 |
|
First Quarter | 21.43 |
| | 15.36 |
|
2012 | | | |
Fourth Quarter | 16.51 |
| | 11.84 |
|
Third Quarter | 17.40 |
| | 14.18 |
|
Second Quarter | 18.22 |
| | 13.59 |
|
First Quarter | 18.13 |
| | 14.17 |
|
Holders of the Corporation’s Capital Stock
We had approximately 494 shareholders of record as of February 3, 2014. This number does not include shareholders for whom shares were held in “nominee” or “street name.”
Dividends
No cash dividends have been declared on our common stock to date nor have any decisions been made to pay a dividend in the future. Payment of dividends is evaluated on a periodic basis and if a dividend were paid, it would be subject to the covenants of our revolving credit facility, which may have the effect of restricting our ability to pay dividends.
Stock Repurchases
The table below includes repurchases of our common stock pursuant to publicly announced plans or programs and those not made pursuant to publicly announced plans or programs during the thirteen weeks ended December 27, 2013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Period | Total number
of shares
purchased (1) | | Weighted average price paid per share (2) | | Total number of shares
purchased as part of
publicly announced plans
or programs | | Maximum number of shares (or approximate dollar value) that may yet be purchased under plans or programs at period end (3) |
09/28/13 through 10/25/13 | 918 |
| | $ | 25.78 |
| | — |
| | $35.2 million |
10/26/13 through 11/22/13 | 1,769 |
| | $ | 24.29 |
| | — |
| | $35.2 million |
11/23/13 through 12/27/13 | 3,239 |
| | $ | 22.94 |
| | — |
| | $35.2 million |
Total | 5,926 |
| | $ | 24.52 |
| | — |
| | |
____________________
| |
(1) | During the thirteen weeks ended December 27, 2013, we purchased 5,926 shares in order to satisfy employee tax withholding obligations upon the vesting of restricted stock. These shares were not acquired pursuant to any publicly announced purchase plan or program. |
| |
(2) | Weighted average price paid per share does not include any adjustments for commissions. |
| |
(3) | Our Board of Directors authorized a $75 million share repurchase program in July 2011 that does not have an expiration date. As of December 27, 2013, $35.2 million remains available for repurchase of our common stock under the current authorization. |
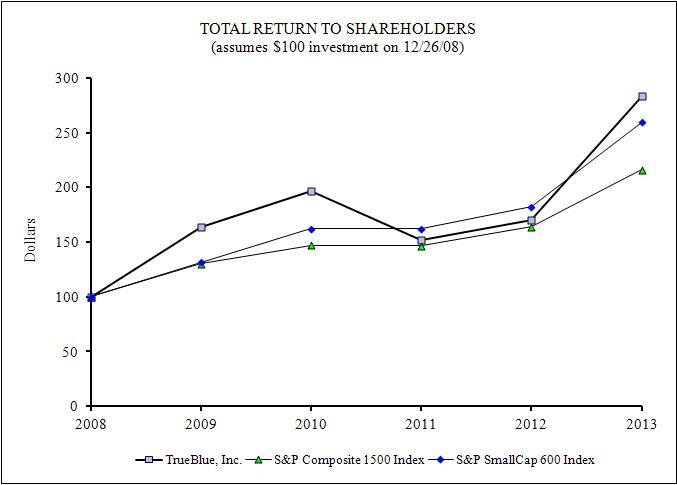
TrueBlue Stock Comparative Performance Graph
The following graph depicts our stock price performance from December 26, 2008 through December 27, 2013, relative to the performance of the S&P SmallCap 600 Index, and a peer group of companies in the temporary staffing industry we have selected in good faith. All indices shown in the graph have been reset to a base of 100 as of December 26, 2008, and assume an investment of $100 on that date and the reinvestment of dividends, if any, paid since that date. The returns of each company in our selected peer group have been weighted to reflect relative stock market capitalization at the beginning of each annual period plotted.
COMPARISON OF 5-YEAR CUMULATIVE TOTAL RETURN
Among TrueBlue, Inc., the S&P SmallCap 600 Index
and Selected Peer Group
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Return Analysis | 2008 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2013 |
TrueBlue, Inc. | $ | 100 |
| | $ | 164 |
| | $ | 197 |
| | $ | 152 |
| | $ | 170 |
| | $ | 283 |
|
Peer Group (1) | $ | 100 |
| | $ | 191 |
| | $ | 212 |
| | $ | 137 |
| | $ | 170 |
| | $ | 282 |
|
S&P SmallCap 600 Index | $ | 100 |
| | $ | 132 |
| | $ | 162 |
| | $ | 162 |
| | $ | 182 |
| | $ | 259 |
|
| |
(1) | The peer group includes Kelly Services, Inc., Manpower, Inc., Robert Half International Inc., Adecco SA and Randstad. |
| |
Item 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The following selected consolidated financial information has been derived from our audited Consolidated Financial Statements. The data should be read in conjunction with Item 1A “Risk Factors,” Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our Consolidated Financial Statements and the notes included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Summary Consolidated Financial and Operating Data
As of and for the Fiscal Year Ended (1)
(in millions, except per share data and number of branches)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013
(52 Weeks) | | 2012
(52 Weeks) | | 2011
(52 Weeks) | | 2010
(53 Weeks) | | 2009
(52 Weeks) |
Statements of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue from services | $ | 1,668.9 |
| | $ | 1,389.5 |
| | $ | 1,316.0 |
| | $ | 1,149.4 |
| | $ | 1,018.4 |
|
Cost of services | 1,226.6 |
| | 1,017.1 |
| | 969.0 |
| | 845.9 |
| | 727.4 |
|
Gross profit | 442.3 |
| | 372.4 |
| | 347.0 |
| | 303.5 |
| | 291.0 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 362.2 |
| | 300.5 |
| | 282.8 |
| | 258.8 |
| | 262.2 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 20.5 |
| | 18.9 |
| | 16.4 |
| | 16.5 |
| | 17.0 |
|
Interest and other income, net | 1.3 |
| | 1.6 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 0.9 |
| | 2.3 |
|
Income before tax expenses | 60.9 |
| | 54.6 |
| | 49.3 |
| | 29.1 |
| | 14.1 |
|
Income tax expense | 16.0 |
| | 21.0 |
| | 18.5 |
| | 9.3 |
| | 5.3 |
|
Net income | $ | 44.9 |
| | $ | 33.6 |
| | $ | 30.8 |
| | $ | 19.8 |
| | $ | 8.8 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Net income per basic share | $ | 1.12 |
| | $ | 0.85 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
| | $ | 0.46 |
| | $ | 0.21 |
|
Net income per diluted share | $ | 1.11 |
| | $ | 0.84 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
| | $ | 0.46 |
| | $ | 0.20 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average diluted shares outstanding | 40.5 |
| | 39.9 |
| | 42.3 |
| | 43.5 |
| | 43.0 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| At Fiscal Year End, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 |
Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | |
Working capital | $ | 235.0 |
| | $ | 203.6 |
| | $ | 168.3 |
| | $ | 207.6 |
| | $ | 163.2 |
|
Total assets | $ | 719.5 |
| | $ | 601.7 |
| | $ | 560.8 |
| | $ | 546.5 |
| | $ | 518.1 |
|
Long-term liabilities | $ | 204.7 |
| | $ | 154.5 |
| | $ | 154.9 |
| | $ | 147.8 |
| | $ | 147.9 |
|
Total liabilities | $ | 326.1 |
| | $ | 268.1 |
| | $ | 267.2 |
| | $ | 233.8 |
| | $ | 232.7 |
|
Branches open at period end | 757 |
| | 691 |
| | 712 |
| | 721 |
| | 754 |
|
| |
(1) | Our fiscal year ends on the last Friday in December. The 2013 fiscal year ended on December 27, 2013, included 52 weeks. The 2010 fiscal year ended on December 31, 2010, included 53 weeks, with the 53rd week falling in our fourth fiscal quarter. All other prior years presented included 52 weeks. |
The operating results reported above include the results of acquisitions subsequent to their respective purchase dates. In February 2013, we acquired substantially all of the net assets of MDT Personnel, LLC. In June 2013, we acquired certain assets of Crowley Transportation Services, LLC. In October 2013, we acquired substantially all of the net assets of The Work Connection, Inc.
No cash dividends have been declared on our common stock to date nor have any decisions been made to pay a dividend in the future.
| |
Item 7. | MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with, and is qualified in its entirety by, the Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes thereto included in Item 8 in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. This item contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ materially from those indicated in such forward-looking statements. Factors that may cause such a difference include, but are not limited to, those discussed in “Item 1A, Risk Factors.”
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (“MD&A”) is designed to provide the reader of our financial statements with a narrative from the perspective of management on our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and certain other factors that may affect future results. Our MD&A is presented in six sections:
| |
• | Liquidity and Capital Resources |
| |
• | Contractual Obligations and Commitments |
| |
• | Summary of Critical Accounting Estimates |
| |
• | New Accounting Standards |
OVERVIEW
TrueBlue is a leading provider of temporary blue-collar staffing and helps over 130,000 businesses be more productive through easy access to dependable temporary labor. We provide specialized blue-collar staffing solutions to industries that include construction, manufacturing, transportation, aviation, waste, hospitality, retail, renewable energy, and more. We connect approximately 375,000 people to work annually through our 757 branches, customer on-site locations generally dedicated to one customer, and national service centers across the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico.
Revenue grew to $1.7 billion for 2013, a 20.1% increase compared to the prior year. The increase is primarily due to revenue earned from acquisitions. Additionally, we experienced strong organic growth in demand for our services across all geographies and industries we serve with a continued increase in construction. The increases in demand and revenue mix have largely offset an expected drop in revenue from a large aviation customer project that is nearing completion.
Effective February 4, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of MDT Personnel, LLC ("MDT"), the third-largest general-labor staffing provider in the United States. Through its network of 105 branches in 25 states, MDT supplied blue-collar labor to industries similar to those served by TrueBlue. We have completed the integration of MDT, which was primarily integrated with our Labor Ready service line. We consolidated 65 branch locations, blended our sales and service teams, integrated all former MDT locations into our enterprise systems, and transitioned MDT support services to our headquarters in Tacoma, Washington.
Effective October 1, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of The Work Connection, Inc. ("TWC"), a light industrial staffing provider with 37 branches located predominantly in the Midwest. TWC’s operations were primarily integrated with those of our Spartan Staffing service line during the fourth quarter ended December 27, 2013. This acquisition expands the geographic reach of Spartan Staffing into new markets.
Gross profit as a percentage of revenue for fiscal 2013 was 26.5%, a decrease of 0.3% compared to the same period in 2012. The decrease is due to the impact of the acquisition of MDT and TWC, which carried lower gross margins in comparison with our blended company average, offset by the favorable impact from disciplined management of bill rates and revenue mix.
Selling, general, and administrative expenses as a percentage of revenue increased to 21.7% for fiscal 2013 as compared to 21.6% for the same period in 2012. This increase is primarily due to the non-recurring costs of $7.4 million of acquisition and integration-related activities net of the benefit of leveraging additional revenue across the fixed costs in our business.
We completed the deployment of our new mobile dispatch technology during 2013. This is proving to drive productivity gains by increasing the number and quality of our applicant pool as well as the number and speed with which jobs are filled. Our ability to reach a wide range of applicants has expanded the geographic reach of our branches and increase our operating efficiency by consolidating local branches.
Net income grew by 33.6% to $44.9 million, or $1.11 per diluted share, for fiscal 2013, compared to a net income of $33.6 million, or $0.84 per diluted share, for fiscal 2012.
We believe we are in a strong financial position to fund working capital needs for planned 2014 growth and expansion opportunities. We had cash, cash equivalents, and highly liquid marketable securities of $142.7 million at December 27, 2013. As of December 27, 2013, the maximum $80.0 million was available under the Revolving Credit Facility and $6.0 million of letters of credit had been issued against the facility, leaving an unused portion of $74.0 million.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following table presents selected financial data (in millions, except percentages and per share amounts):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Revenue from services | $ | 1,668.9 |
| | $ | 1,389.5 |
| | $ | 1,316.0 |
|
Total revenue growth % | 20.1 | % | | 5.6 | % | | 14.5 | % |
| | | | | |
Gross profit as a % of revenue | 26.5 | % | | 26.8 | % | | 26.4 | % |
| | | | | |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | $ | 362.2 |
| | $ | 300.5 |
| | $ | 282.8 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses as a % of revenue | 21.7 | % | | 21.6 | % | | 21.5 | % |
| | | | | |
Income from operations | $ | 59.6 |
| | $ | 53.0 |
| | $ | 47.8 |
|
Income from operations as a % of revenue | 3.6 | % | | 3.8 | % | | 3.6 | % |
| | | | | |
Net income | $ | 44.9 |
| | $ | 33.6 |
| | $ | 30.8 |
|
Net income per diluted share | $ | 1.11 |
| | $ | 0.84 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
|
Effective February 4, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of MDT, the third-largest general-labor staffing provider in the United States. MDT supplied blue-collar labor to industries similar to those served by TrueBlue, including construction, event staffing, disaster recovery, hospitality, and manufacturing through its network of 105 branches in 25 states. MDT operations were primarily integrated with our Labor Ready service line. We consolidated 65 branch locations, blended our sales and service teams, and fully integrated all former MDT locations into our enterprise systems. The acquisition of MDT has both deepened our expertise and strengthened our position in the key industries we serve. The customers of MDT have been fully integrated with our existing customer base and are serviced by our blended operations. We completed the integration of all remaining administrative services during the second quarter of 2013. Due to full consolidation of the MDT branches, blending our sales and service teams, and fully integrating all former MDT locations into our enterprise systems, we cannot accurately segregate the acquisition revenue from our organic revenue growth.
Effective October 1, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of TWC, a light industrial staffing provider with 37 branches located predominantly in the Midwest with minimal overlap with existing TrueBlue branch offices. TWC delivered specialized blue-collar staffing solutions for more than 25 years to customers in industries similar to those served by TrueBlue. TWC’s operations were primarily integrated with those of our Spartan Staffing service line during the fourth quarter of this year.
We also acquired certain assets of Crowley Transportation Services, LLC ("CTS") in June 2013. The total cost of the acquisition was $2.4 million, including contingent consideration of $0.6 million. CTS was founded in 2003 and provided full service transportation staffing servicing primarily the northeastern part of the United States. This acquisition provides us geographic expansion into six new states for our Centerline Drivers service line. The CTS operations were integrated with the Centerline Drivers service line during the second quarter ended June 28, 2013.
The decision to acquire MDT, TWC and CTS's operations reflects our overall optimism about growth in the staffing industry and our continued business strategy to expand current market share through acquisitions. These acquisitions enhance TrueBlue's national position as the leading provider of dependable blue-collar temporary labor, which we expect will generate further synergies from the fully integrated operations with our existing service lines.
Revenue
Revenue from services was as follows (in millions, except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Revenue from services | $ | 1,668.9 |
| | $ | 1,389.5 |
| | $ | 1,316.0 |
|
Total revenue growth % | 20.1 | % | | 5.6 | % | | 14.5 | % |
Fiscal 2013 as compared to fiscal 2012
Revenue grew to $1.7 billion for fiscal 2013, a 20.1% increase compared to the prior year. The increase was primarily due to revenue resulting from the acquisition of MDT in the first quarter of 2013 and TWC in the fourth quarter of 2013. Additionally, we experienced strong organic growth in demand for our services across all geographies and industries we serve with a continued increase in construction. The increases in demand and revenue mix have largely offset an expected drop in revenue from a large aviation customer project that is nearing completion.
We continue to see success with our focus on generating strong organic growth by making it easier for our customers to access reliable workers and for our workers to access work opportunities. We improve the productivity of our customers with temporary staffing solutions which are specialized and tailored to their needs. We have made substantial investments in technology solutions that improve both the customer and worker experience as well as our business efficiency.
Fiscal 2012 as compared to 2011
Revenue grew to $1.4 billion for fiscal 2012, a 5.6% increase compared to the prior year. Revenue growth slowed in the second half of 2012 due to manufacturing declines, softening growth trends across the business, and lower revenue from a large customer. Services related to this large customer are project based and had been declining throughout the year as the project matured and our customer made workforce adjustments. Our revenue growth is also due to the continued success of our specialized market sales and service strategy. Our dedicated sales leaders have expertise in the specific industries we serve. They partner with our service teams to meet the specific project needs of our national customers. Likewise, they provide our branches with best practice industry knowledge including sales and service methods for each industry. Our local sales and service teams build strong customer relationships and loyalty in providing tailored solutions that meet the day to day needs of our local customers. We have experienced continued success in renewable energy construction projects along with an improving construction market.
Gross profit
Gross profit was as follows (in millions, except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Gross profit | $ | 442.3 |
| | $ | 372.4 |
| | $ | 347.0 |
|
Percentage of revenue | 26.5 | % | | 26.8 | % | | 26.4 | % |
Fiscal 2013 as compared to fiscal 2012
Gross profit represents revenues from services less direct costs of services, which consist of payroll, payroll taxes, workers' compensation costs, and reimbursable costs. Gross profit as a percentage of revenue for fiscal 2013 of 26.5% decreased by 0.3% compared to the prior year. The decrease is primarily due to the acquisition of MDT and TWC, which carried lower gross margins in comparison with our blended company average, largely offset by the favorable impact from disciplined pricing and revenue mix.
Workers’ compensation expense as a percentage of revenue remained constant at 3.8% for fiscal 2013 compared to the prior year. We actively manage the safety of our temporary workers with our risk management programs and work together with our network of service providers to control costs. MDT and TWC have been fully integrated into our workers' compensation insurance and safety programs.
Fiscal 2012 as compared to fiscal 2011
Gross profit as a percentage of revenue improved by 0.4% for fiscal 2012 primarily due to increased bill rates which more than offset increases to minimum wages and unemployment taxes in 2012. Our team continued to leverage our specialized approach in the blue-collar market along with disciplined pricing to drive higher gross margin. We are selective in the customers we serve and diligent in our approach to setting appropriate bill rates.
Workers’ compensation expense as a percentage of revenue was 3.8% for fiscal 2012 compared to 3.9% for 2011. We experienced a further reduction to accidents in 2012 as compared to the prior year through actively managing the safety of our temporary workers and the job site.
Selling, general and administrative expenses
Selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses were as follows (in millions, except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | $ | 362.2 |
| | $ | 300.5 |
| | $ | 282.8 |
|
Percentage of revenue | 21.7 | % | | 21.6 | % | | 21.5 | % |
Fiscal 2013 as compared to fiscal 2012
The increase in SG&A spending of $61.7 million is primarily due to ongoing branch and field management and operating costs associated with the MDT and TWC acquisitions, non-recurring acquisition and integration costs of $7.4 million, and variable SG&A expenses associated with organic revenue growth. The non-recurring acquisition and integration costs consisted of closing, consolidating and relocating certain branch and administrative operations, eliminating redundant assets and reducing excess administrative workforce and capacity together with other integration program costs. Excluding those non-recurring costs, SG&A expenses increased by $54.3 million.
SG&A as a percentage of revenue remained relatively constant at 21.7% for fiscal 2013 as compared to 21.6% for the prior year. Excluding the non-recurring acquisition and integration costs, SG&A as a percentage of revenue for fiscal 2013 decreased to 21.3%. The decrease is due to leveraging our revenue growth across our existing cost structure.
The improvements to our SG&A leverage were partially offset by the anticipated decline in revenue from a large customer. This customer was serviced from a centralized service center with a largely fixed cost structure. Consequently, we did not experience a decline in variable SG&A commensurate with the decline in revenue.
Fiscal 2012 as compared to fiscal 2011
SG&A as a percentage of revenue remained relatively constant at 21.6% for 2012 as compared to 21.5% for the prior year. The increase in SG&A spending of $17.7 million for fiscal 2012 is primarily due to the variable selling and other operating expenses associated with the revenue increase of $73.5 million or 5.6%. Excluding revenue from a large customer, revenue increased $103.8 million or 8.6% over the prior year. This customer was serviced from a centralized service center with a largely fixed cost structure. Consequently, we did not experience a decline in variable SG&A commensurate with the decline in revenue.
We have continued to invest in our specialized vertical market sales and service strategy and projects to further improve our efficiency and effectiveness in recruiting and retaining our temporary workers and attracting and retaining our customers. We completed a major investment in the operating system of our Labor Ready service line during 2012. In 2013 we realized the benefits of this investment through improved operating efficiency.
Depreciation and amortization
Depreciation and amortization were as follows (in millions, except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 20.5 |
| | $ | 18.9 |
| | $ | 16.4 |
|
Percentage of revenue | 1.2 | % | | 1.4 | % | | 1.2 | % |
Fiscal 2013 as compared to 2012
Depreciation and amortization expense remained relatively constant as a percentage of revenue. The 2013 increase over 2012 of $1.6 million is primarily from increased amortization related to the finite-lived intangible and tangible assets acquired through acquisitions. We continue to make significant investments in projects that are designed to further improve our efficiency and effectiveness in recruiting, retaining our temporary workers, and attracting and retaining our customers.
Fiscal 2012 as compared to 2011
Depreciation and amortization for fiscal 2012 increased over the prior year by $2.5 million primarily from increased capital spending on enterprise technology improvement projects. These projects are designed to further improve our efficiency and effectiveness in recruiting and retaining our temporary workers and attracting and retaining our customers.
Interest and other income, net
Net interest and other income was as follows (in millions, except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Interest and other income, net | $ | 1.3 |
| | $ | 1.6 |
| | $ | 1.5 |
|
Percentage of revenue | 0.1 | % | | 0.1 | % | | 0.1 | % |
Net interest income remained relatively flat for the comparative periods.
Income taxes
The effective income tax rate was as follows (in millions, except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Income tax expense | $ | 16.0 |
| | $ | 21.0 |
| | $ | 18.5 |
|
Effective income tax rate | 26.3 | % | | 38.4 | % | | 37.6 | % |
Fiscal 2013 compared to fiscal 2012
Our effective tax rate on earnings for 2013 was 26.3% compared to 38.4% for 2012. The effective tax rate for 2012 excluded benefits of federal Work Opportunity Tax Credit (“WOTC”) because it had largely expired at the end of 2011. The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (the “Act”) was signed into law on January 2, 2013, and retroactively restored the WOTC for 2012 and extended it through 2013. This tax credit is designed to encourage employers to hire workers from certain targeted groups with higher than average unemployment rates. Because a change in the law is accounted for in the period of enactment, the retroactive effect of the Act on our U.S. federal taxes for 2012 was recognized in the year ended December 27, 2013. Accordingly, the decrease in the effective tax rate is due primarily to the benefit of the retroactively restored WOTC. The impact of WOTC on our effective tax rate is greater when our pre-tax income is lower.
The primary difference between the statutory federal income tax rate of 35.0% and our annual effective income tax rate of 26.3%, excluding the prior year WOTC benefits, is from current year WOTC, state income taxes, and certain non-deductible expenses.
Fiscal 2012 compared to fiscal 2011
Our effective tax rate on earnings for 2012 was 38.4% compared to 37.6% for the same period in 2011. The increase in the effective income tax rate is due primarily to WOTC, which largely expired at the end of 2011. The principal difference between the statutory federal income tax rate of 35% and our effective income tax rate results from state income taxes, federal tax credits and certain non-deductible expenses.
Results of Operations Future Outlook
The following highlights represent our expectations regarding operating trends for the fiscal year 2014. These expectations are subject to revision as our business changes with the overall economy:
| |
• | Our top priority is to produce strong organic revenue and gross profit growth and leverage our cost structure to generate increasing operating income as a percentage of revenue. Additionally, we have completed the integration of all acquisitions made during 2013 and accordingly, we do not expect further non-recurring costs associated with these acquisitions. We will continue to invest in our specialized sales, recruiting, and customer service programs, which we believe will enhance our ability to capitalize on further revenue growth and customer retention. We actively pursue large project opportunities in vertical markets with growth opportunities. One of our largest successes is in the construction of renewable energy projects. While our growth rates in renewable energy projects have diminished due to more challenging prior year comparisons, these projects remain an attractive opportunity. |
| |
• | We will continue to pursue other opportunities to grow our share of the blue-collar market through acquisitions and to enhance TrueBlue's national position as the leading provider of dependable blue-collar temporary labor. Acquisitions are |
a key element of our growth strategy. We expect to leverage our cost structure and produce long-term, incremental operating margins by merging the acquired operations with ours and generating synergies. We have been successful at acquiring and integrating companies and believe we have a strong business competence to continue to do so.
| |
• | As the economy grows, we will continue to evaluate opportunities to expand our market presence. All of our multi-location service lines have opportunities to expand through new physical locations or by sharing existing locations. Where possible, we plan to expand the presence of our service lines by sharing existing locations to achieve cost synergies. We plan to build on our success with centralized recruitment and dispatch of our temporary workers to locations without physical branches and expand our geographic reach. |
| |
• | We have been investing in technology solutions. We see compelling opportunities to improve the speed in assigning candidates to jobs and increase the productivity of our branch employees, which we expect will result in the consolidation of branches and other benefits to our cost structure. We deployed our new mobile dispatch technology during 2013 and expect it to enhance our ability to recruit workers and put them on the job faster. The convenience the technology offers our workers and our ability to get them on the job faster will translate into a larger, higher-quality workforce and improved customer sales and service. We plan to continue to expand the use of technology to improve the worker and customer experience as well as our own efficiency. |
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
As of December 27, 2013, our cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities totaled $142.7 million compared to $129.5 million as of December 28, 2012, an increase of $13.2 million. This increase in cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities was primarily driven by cash generated from operations of $86.1 million and proceeds from notes payable of $34.0 million, partially offset by acquisitions of businesses of $77.6 million, and capital expenditures of $13.0 million for the year ended December 27, 2013.
We have investments in various securities, including money market funds, certificates of deposit ("CDs"), variable-rate demand notes (“VRDNs”), and commercial paper, all of which are highly liquid and available to fund operations, strategic growth opportunities, and share buy backs.
The following discussion highlights our cash flow activities for the year ended December 27, 2013.
Cash flows from operating activities
Our cash flows from operating activities were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Net income | $ | 44.9 |
| | $ | 33.6 |
| | $ | 30.8 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash from operating activities: | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | 20.5 |
| | 18.9 |
| | 16.4 |
|
Provision for doubtful accounts | 12.1 |
| | 7.0 |
| | 6.6 |
|
Stock-based compensation | 8.4 |
| | 7.9 |
| | 7.4 |
|
Deferred income taxes | (3.8 | ) | | 3.1 |
| | (1.9 | ) |
Other operating activities | 2.1 |
| | 1.9 |
| | (0.5 | ) |
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | (4.2 | ) | | (20.4 | ) | | (51.8 | ) |
Income taxes | 4.1 |
| | (3.7 | ) | | 3.5 |
|
Accounts payable and other accrued expenses | (7.3 | ) | | 1.3 |
| | 16.2 |
|
Workers' compensation claims reserve | 9.9 |
| | 3.7 |
| | 4.5 |
|
Other assets and liabilities | (0.6 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | (0.6 | ) |
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 86.1 |
| | $ | 52.3 |
| | $ | 30.6 |
|
Our principal source of liquidity is operating cash flows. Our net income and, consequently, our cash provided from operations are impacted by sales volume, timing of collections, seasonal sales patterns and profit margins.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $86.1 million for the year ended December 27, 2013 as compared to $52.3 million for the same period in 2012.
| |
• | The increase in cash from operations is primarily due to net income of $44.9 million. |
| |
• | Amortization expense increased over 2012 by $1.6 million primarily from increased amortization related to the finite-lived intangible and tangible assets acquired through acquisitions. |
| |
• | Accounts receivable increased in fiscal 2013 due primarily to revenue growth which was largely offset by collections of receivables acquired as part of the acquisition of MDT and TWC and improvement to our time to collect. The provision for doubtful accounts increased in 2013 primarily due to revenue growth and an increase in probable credit losses associated primarily with the construction industry. |
| |
• | Accounts payable and other accrued expenses decreased in 2013 primarily due to the payment of nearly all of the acquired accounts payable from our acquisitions during the year, partially offset by increased wages due to growth and higher payroll tax rates. |
| |
• | Generally our workers' compensation reserve for estimated claims increases as temporary labor services increase and decreases as temporary labor services decline. During the current year, our workers' compensation reserve increased as we increased the delivery of temporary labor services, which was partially offset by claim payments. |
Cash flows from investing activities
Our cash flows from investing activities were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Capital expenditures | $ | (13.0 | ) | | $ | (17.8 | ) | | $ | (9.7 | ) |
Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | (77.6 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Purchases of marketable securities | (40.8 | ) | | — |
| | |
Sales and maturities of marketable securities | 20.0 |
| | — |
| | |
Change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | (16.1 | ) | | 7.6 |
| | 68.5 |
|
Purchase of restricted investments | (13.4 | ) | | (33.8 | ) | | (88.2 | ) |
Maturities of restricted investments | 15.6 |
| | 18.1 |
| | 9.3 |
|
Other | — |
| | (0.3 | ) | | (6.8 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | $ | (125.3 | ) | | $ | (26.2 | ) | | $ | (26.9 | ) |
| |
• | Cash flows used in investing activities increased primarily due to acquisitions. Effective February 4, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of MDT for $53.4 million in cash. MDT supplied blue-collar labor to industries similar to those served by TrueBlue, including construction, event staffing, disaster recovery, hospitality, and manufacturing through its network of 105 branches in 25 states. We fully integrated and blended MDT's operations with our existing service lines. MDT was primarily integrated into the Labor Ready service line. The integration of the MDT sales and branch operations was completed during the first quarter of 2013. We consolidated 65 branches, blended our sales and service teams and fully integrated all former MDT locations into our enterprise systems to optimize our combined operational efficiencies during the first quarter of 2013. We completed the integration of all remaining administrative services during the second quarter ended June 28, 2013. |
We acquired certain assets and liabilities of TWC in October 2013. The total cost of the acquisition was $22.7 million. TWC was founded in 1986 and provided light industrial services out of 37 branches in nine states. This acquisition provides geographic expansion into new markets for our Spartan Staffing service line. TWC’s operations were integrated with those of our Spartan Staffing service line during the fourth quarter ended December 27, 2013.
We also acquired certain assets of Crowley in June 2013. The total cost of the acquisition was $2.4 million, including contingent consideration of $0.6 million.
| |
• | Marketable securities consist of CDs, VRDNs, and commercial paper, which are classified as available-for-sale. VRDNs are long-term municipal and corporate securities with an interest rate that is reset frequently. All the VRDNs currently in our portfolio are backed by a bank Letter of Credit. Our VRDNs may be tendered at any time with a typical settlement date of less than one week. We did not hold any marketable securities at December 28, 2012. |
| |
• | Restricted cash and investments consist primarily of collateral that has been provided or pledged to insurance carriers and state workers' compensation programs. The change in restricted cash and cash equivalents is primarily a product of purchasing restricted investments, maturities on restricted investments, and payments to workers' compensation insurance providers. When combining this change with purchases of restricted investments net of maturities of restricted investments, restricted cash and investments increased by $14.0 million for the year ended December 27, 2013. This increase is primarily |
due to an increase in the collateral requirements by our workers' compensation insurance providers related to growth in operations, which was partially offset by claim payments.
| |
• | Capital spending decreased as we completed a major investment in the operating system of our Labor Ready service line during 2012. In 2013 we realized the benefits of this investment through improved operating efficiency. We completed the full deployment of our new mobile dispatch technology during mid 2013. This is proving to drive productivity gains by increasing the number and quality of our applicant pool as well as the number and speed with which jobs are filled. Our ability to reach a wide range of applicants has expanded the geographic reach of our branches and provided the opportunity to reduce occupancy costs by consolidating local branches and increasing our operating efficiency. The convenience this technology offers our workers, and our ability to get them on the job faster will translate into a larger, higher-quality workforce and improved customer sales and service. We continue to invest in projects that are designed to further improve our efficiency and effectiveness in recruiting and retaining our temporary workers and attracting and retaining our customers. |
Cash flows from financing activities
Our cash flows from financing activities were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Purchases and retirement of common stock | $ | — |
| | $ | (4.4 | ) | | $ | (56.9 | ) |
Net proceeds from stock option exercises and employee stock purchase plans | 9.1 |
| | 4.2 |
| | 1.1 |
|
Common stock repurchases for taxes upon vesting of restricted stock | (2.8 | ) | | (2.2 | ) | | (1.8 | ) |
Proceeds from note payable | 34.0 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Payments on debt and other liabilities | (8.6 | ) | | (4.5 | ) | | (0.3 | ) |
Other | 0.7 |
| | 0.7 |
| | 0.7 |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | $ | 32.4 |
| | $ | (6.2 | ) | | $ | (57.2 | ) |
The change in cash provided by financing activities was mainly due to proceeds from our Term Loan Agreement with Synovus Bank of $34.0 million in connection with our acquisition of MDT.
Future outlook
Our cash-generating capability provides us with substantial financial flexibility in meeting our operating and investing needs. We believe we are in a strong financial position to fund working capital needs for planned growth. The strength of our current financial position is highlighted as follows:
| |
• | We had cash, cash equivalents and highly liquid marketable securities of $142.7 million at December 27, 2013. |
| |
• | Our borrowing availability under our credit facility is principally based on accounts receivable and the value of our corporate building. We have $74.0 million of borrowing available under our credit facility as of December 27, 2013. We believe the credit facility provides adequate borrowing availability. |
| |
• | The majority of our workers’ compensation payments are made from restricted cash rather than cash from operations. |
We believe that cash provided from operations and our capital resources will be adequate to meet our cash requirements for the foreseeable future.
Capital resources
We have a credit agreement with Bank of America, N.A. and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC for a secured revolving credit facility of up to a maximum of $80.0 million (the “Revolving Credit Facility”). The Revolving Credit Facility expires in September 2016.
The maximum amount we can borrow under the Revolving Credit Facility is subject to certain borrowing limits. Specifically, we are limited to the sum of 85% of our eligible accounts receivable and the liquidation value of our Tacoma headquarters office building. The liquidation value is not to exceed $15.0 million, and is reduced quarterly by $0.4 million. As of December 27, 2013, the Tacoma headquarters office building liquidation value totaled $12.0 million. This borrowing limit is further reduced by the sum of a reserve in an amount equal to the payroll and payroll taxes for our temporary employees for one payroll cycle and other reserves, if deemed applicable. As of December 27, 2013, the maximum $80.0 million was available and letters of credit in the amount of $6.0 million had been issued against the facility, leaving an unused portion of $74.0 million. The letters of credit collateralize a portion of our workers' compensation obligation.
The Revolving Credit Facility requires that we maintain liquidity in excess of $12.0 million. Liquidity is defined as the amount we are entitled to borrow as advances under the Revolving Credit Facility plus the amount of cash, cash equivalents and certain marketable securities held in accounts subject to a control agreement benefiting the lenders. We are required to satisfy a fixed charge coverage ratio in the event we do not meet that requirement. The amount we were entitled to borrow at December 27, 2013 was $74.0 million and the amount of cash, cash equivalents and certain marketable securities under control agreements was $124.5 million for a total of $198.5 million of liquidity, which is well in excess of the minimum liquidity requirement. We are currently in compliance with all covenants related to the Revolving Credit Facility.
Under the terms of the Revolving Credit Facility, we pay a variable rate of interest on funds borrowed that is based on LIBOR or the Prime Rate, at our option, plus an applicable spread based on excess liquidity as set forth below:
|
| | | | |
Excess Liquidity | | Prime Rate Loans | | LIBOR Rate Loans |
Greater than $40 million | | 0.50% | | 1.50% |
Between $20 million and $40 million | | 0.75% | | 1.75% |
Less than $20 million | | 1.00% | | 2.00% |
A fee on borrowing availability of 0.25% is also applied against the unused portion of the Revolving Credit Facility. Letters of credit are priced at the margin in effect for LIBOR loans, plus a fronting fee of 0.125%.
Obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are secured by substantially all of our domestic personal property and our headquarters located in Tacoma, Washington.
We have agreements with certain financial institutions that allow us to restrict cash and cash equivalents and investments for the purpose of providing collateral instruments to our insurance carriers to satisfy workers' compensation claims. At December 27, 2013, we had restricted cash and investments totaling approximately $154.6 million.
In 2011, we entered into an agreement with AIG and the Bank of New York Mellon creating a trust ("Trust"), which holds the majority of our collateral obligations under existing workers' compensation insurance policies. We established investment policy directives for the Trust, with the first priority to ensure sufficient liquidity to pay workers' compensation claims, second to maintain and ensure a high degree of liquidity, and third to maximize after-tax returns.
Trust investments must meet minimum acceptable quality standards. The primary investments include U.S. Treasury Securities, U.S. Agency Debentures, U.S. Agency Mortgages, Corporate Securities, and Municipal Securities. For those investments rated by the Nationally Recognized Statistical Rating Organizations the minimum ratings are:
|
| | | | | | |
| | S&P | | Moody's | | Fitch |
Short-term Rating | | A-1/SP-1 | | P-1/MIG-1 | | F-1 |
Long-term Rating | | A | | A2 | | A |
Workers’ compensation insurance, collateral and claims reserves
Workers' compensation insurance
We provide workers’ compensation insurance for our temporary and permanent employees. The majority of our current workers’ compensation insurance policies cover claims for a particular event above a $2.0 million deductible limit, on a “per occurrence” basis. This results in our being substantially self-insured.
In connection with the acquisition of MDT, we assumed certain workers' compensation insurance policies, which cover claims for the policy year ended February 13, 2013.
For workers’ compensation claims originating in Washington, North Dakota, Ohio, Wyoming, Canada and Puerto Rico (our “monopolistic jurisdictions”), we pay workers’ compensation insurance premiums and obtain full coverage under government-administered programs (with the exception of our Labor Ready service line in the state of Ohio where we have a self-insured policy). Accordingly, because we are not the primary obligor, our financial statements do not reflect the liability for workers’ compensation claims in these monopolistic jurisdictions.
Workers' compensation collateral
Our insurance carriers and certain state workers’ compensation programs require us to collateralize a portion of our workers’ compensation obligation, for which they become responsible should we become insolvent. The collateral typically takes the form of cash and cash-backed instruments, highly rated investment grade securities, letters of credit, and/or surety bonds. On a regular basis, these entities assess the amount of collateral they will require from us relative to our workers’ compensation obligation. Such amounts can increase or decrease independent of our assessments and reserves. We generally anticipate that our collateral commitments will continue to grow as we grow our business. We pay our premiums and deposit our collateral in installments. The majority of the restricted cash and investments collateralizing our self-insured workers' compensation policies are held in the Trust.
Our total collateral commitments were made up of the following components (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 |
Cash collateral held by insurance carriers | $ | 23.7 |
| | $ | 21.5 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents held in Trust (1) | 31.5 |
| | 14.8 |
|
Investments held in Trust | 86.7 |
| | 91.2 |
|
Letters of credit (2) | 7.9 |
| | 9.0 |
|
Surety bonds (3) | 16.1 |
| | 16.2 |
|
Total collateral commitments | $ | 165.9 |
| | $ | 152.7 |
|
| |
(1) | Included in this amount is $0.8 million and $0.9 million of accrued interest at December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. |
| |
(2) | We have agreements with certain financial institutions to issue letters of credit as collateral. We had $1.9 million and $1.8 million of restricted cash collateralizing our letters of credit as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012. |
| |
(3) | Our surety bonds are issued by independent insurance companies on our behalf and bear annual fees based on a percentage of the bond, which is determined by each independent surety carrier. These fees do not exceed 2.0% of the bond amount, subject to a minimum charge. The terms of these bonds are subject to review and renewal every one to four years and most bonds can be canceled by the sureties with as little as 60 days' notice. |
Workers' compensation reserve
The following table provides a reconciliation of our collateral commitments to our workers’ compensation reserve as of the period end dates presented (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 |
Total workers’ compensation reserve | $ | 214.8 |
| | $ | 195.6 |
|
Add back discount on workers' compensation reserve (1) | 19.6 |
| | 20.4 |
|
Less excess claims reserve (2) | (34.1 | ) | | (26.9 | ) |
Reimbursable payments to insurance provider (3) | 9.5 |
| | 6.4 |
|
Less portion of workers' compensation not requiring collateral (4) | (43.9 | ) | | (42.8 | ) |
Total collateral commitments | $ | 165.9 |
| | $ | 152.7 |
|
| |
(1) | Our workers’ compensation reserves are discounted to their estimated net present value while our collateral commitments are based on the gross, undiscounted reserve. |
| |
(2) | Excess claims reserve includes the estimated obligation for claims above our deductible limits. These are the responsibility of the insurance carriers against which there are no collateral requirements. |
| |
(3) | This amount is included in restricted cash and represents a timing difference between claim payments made by our insurance carrier and the reimbursement from cash held in the Trust. When claims are paid by our carrier, the amount is removed from the workers' compensation reserve but not removed from collateral until reimbursed to the carrier. |
| |
(4) | Represents deductible and self-insured reserves where collateral is not required. |
Our workers’ compensation reserve is established using estimates of the future cost of claims and related expenses, which are discounted to their estimated net present value. The discounted workers’ compensation claims reserve was $214.8 million at December 27, 2013.
Our workers' compensation reserve for self-insured claims is established using estimates of the future cost of claims and related expenses that have been reported but not settled, as well as those that have been incurred but not reported. Reserves are estimated for claims incurred in the current year, as well as claims incurred during prior years. Management evaluates the adequacy of the
workers’ compensation reserves in conjunction with an independent quarterly actuarial assessment. Factors considered in establishing and adjusting these reserves include, among other things:
| |
• | Changes in medical and time loss (“indemnity”) costs; |
| |
• | Mix changes between medical only and indemnity claims; |
| |
• | Regulatory and legislative developments impacting benefits and settlement requirements; |
| |
• | Type and location of work performed; |
| |
• | The impact of safety initiatives; and |
| |
• | Positive or adverse development of claims. |
Our workers’ compensation claims reserves are discounted to their estimated net present value using discount rates based on returns of “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments with maturities comparable to the weighted average lives of our workers’ compensation claims. At December 27, 2013, the weighted average rate was 2.1%. The claim payments are made over an estimated weighted average period of approximately 5.5 years.
Our workers’ compensation reserves include estimated expenses related to claims above our self-insured limits (“excess claims”), and a corresponding receivable for the insurance coverage on excess claims based on the contractual policy agreements we have with insurance carriers. We discount this reserve and corresponding receivable to its estimated net present value using the discount rates based on average returns of “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments available during the year in which the liability was incurred. At December 27, 2013, the weighted average rate was 3.9%. The claim payments are made and the corresponding reimbursements from our insurance carriers are received over an estimated weighted average period of approximately 15.5 years. The discounted workers’ compensation reserve for excess claims and the corresponding receivable for the insurance on excess claims were $34.1 million and $27.1 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively.
The following table provides an analysis of changes in our workers’ compensation claims reserves (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Beginning balance | $ | 195.6 |
| | $ | 191.8 |
| | $ | 187.3 |
|
Self-insurance reserve expenses related to current year, net (1) | 68.2 |
| | 55.7 |
| | 52.4 |
|
Payments related to current year claims (2) | (14.8 | ) | | (11.3 | ) | | (11.2 | ) |
Payments related to claims from prior years (2) | (34.3 | ) | | (26.9 | ) | | (29.3 | ) |
Changes to prior years’ self-insurance reserve, net (3) | (19.1 | ) | | (13.7 | ) | | (16.9 | ) |
Amortization of prior years’ discount (4) | 3.8 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 7.9 |
|
Net change in excess claims reserve (5) | 7.0 |
| | (0.2 | ) | | 1.6 |
|
Liability assumed from acquired business, net (6) | 8.4 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Ending balance | 214.8 |
| | 195.6 |
| | 191.8 |
|
Less current portion | 49.9 |
| | 44.7 |
| | 43.5 |
|
Long-term portion | $ | 164.9 |
| | $ | 150.9 |
| | $ | 148.3 |
|
| |
(1) | Our self-insurance reserves are discounted to their estimated net present value using discount rates based on returns of “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments with maturities comparable to the weighted average lives of our workers’ compensation claims. At December 27, 2013, the weighted average rate was 2.1%. |
| |
(2) | Payments made against self-insured claims are made over a weighted average period of approximately 5.5 years. |
| |
(3) | Changes in reserve estimates are reflected in the statement of operations in the period when the changes in estimates are made. |
| |
(4) | Amortization of discount over the estimated weighted average life. In addition, any changes to the estimated weighted average lives and corresponding discount rates for actual payments made are reflected in the statement of operations in the period when the changes in estimates are made. |
| |
(5) | Changes to the workers' compensation reserve for claims above our self-insured limits (“excess claims”) net of discount to its estimated net present value using the risk-free rates associated with the actuarially determined weighted average lives of our excess claims. At December 27, 2013, the weighted average rate was 3.9%. The excess claim payments are made and the corresponding reimbursements from our insurance carriers are received over a weighted average period of approximately 15.5 years. Certain workers’ compensation insurance companies with which we formerly did business are in liquidation and have failed to pay a number of excess claims to date. We have recorded a valuation allowance against all of the insurance receivables from the insurance companies in liquidation. |
| |
(6) | Effective February 4, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of MDT, including $9.4 million of workers' compensation liability. As of December 27, 2013, we have paid approximately $1.0 million of the liability. See Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS AND COMMITMENTS
The following table provides a summary of our contractual obligations as of the end of fiscal 2013. We expect to fund these commitments with existing cash and cash equivalents, and cash flows from operations.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments Due by Period (in millions) |
Contractual Obligations | Total | | 2014 | | 2015
through
2016 | | 2017
through
2018 | | 2019
and
later |
Long-term debt obligations (1) | $ | 32.0 |
| | $ | 2.3 |
| | $ | 4.6 |
| | $ | 25.1 |
| | $ | — |
|
Operating leases (2) | 3.6 |
| | 1.8 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 0.3 |
| | — |
|
Purchase obligations (3) | 16.8 |
| | 8.9 |
| | 7.6 |
| | 0.3 |
| | — |
|
Total contractual cash obligations | $ | 52.4 |
| | $ | 13.0 |
| | $ | 13.7 |
| | $ | 25.7 |
| | $ | — |
|
| |
(1) | Long-term debt obligations represent our scheduled debt maturities on our unsecured Term Loan Agreement with Synovus Bank. For additional information, see Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
| |
(2) | Excludes all payments related to branch leases cancelable within 90 days. For additional information, see Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
| |
(3) | Purchase obligations include agreements to purchase goods and services that are enforceable, legally binding, and specify all significant terms. Purchase obligations do not include agreements that are cancelable without significant penalty. |
Liability for unrecognized tax benefits has been excluded from the table above, as the timing and/or amounts of any cash payment is uncertain. For additional information, see Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
SUMMARY OF CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations discusses our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. On an ongoing basis, management evaluates its estimates and judgments. Management bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Management believes that the following accounting estimates are the most critical to aid in fully understanding and evaluating our reported financial results, and they require management’s most difficult, subjective, or complex judgments, resulting from the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain.
Workers’ compensation reserves
We maintain reserves for workers’ compensation claims, including the excess claims portion above our deductible, using actuarial estimates of the future cost of claims and related expenses. These estimates include claims that have been reported but not settled and claims that have been incurred but not reported. These reserves, which reflect potential liabilities to be paid in future periods based on estimated payment patterns, are discounted to estimated net present value using discount rates based on average returns on “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments, which are evaluated on a quarterly basis. We evaluate the reserves regularly throughout the year and make adjustments accordingly. If the actual cost of such claims and related expenses exceeds the amounts estimated, additional reserves may be required. Changes in reserve estimates are reflected in the statement of operations in the period when the changes in estimates are made.
Our workers’ compensation reserves include estimated expenses related to claims above our self-insured limits (“excess claims”) and a corresponding receivable for the insurance coverage on excess claims based on the contractual policy agreements we have with insurance companies. We discount the reserve and its corresponding receivable to its respective estimated net present value using the risk-free rates associated with the actuarially determined weighted average lives of our excess claims. When appropriate,
based on our best estimate, we record a valuation allowance against the insurance receivable to reflect amounts that may not be realized.
There are two main factors that impact workers’ compensation expense: the number of claims and the cost per claim. The number of claims is driven by the volume of hours worked, the business mix which reflects the type of work performed, and the safety of the environment where the work is performed. The cost per claim is driven primarily by the severity of the injury, the state in which the injury occurs, related medical costs, and lost-time wage costs. A 5% change in the cost of claims incurred would result in a change to workers' compensation expense of approximately $8.8 million. We have not had significant changes in the assumptions used in calculating our reserve balance. Our reserve balances have been positively impacted primarily by the success of our accident prevention programs. In the event that we are not able to further reduce our accident rates, the positive impacts to our reserve balance will diminish.
Allowance for doubtful accounts
We establish an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the failure of our customers to make required payments. The allowance for doubtful accounts is determined based on historical write-off experience, expectations of future write-offs and current economic data, and represents our best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses. The allowance for doubtful accounts is reviewed quarterly and past due balances are written-off when it is probable the receivable will not be collected. If the financial condition of our customers were to deteriorate, resulting in an impairment of their ability to make payments, additional allowances may be required.
Goodwill and intangible assets
Goodwill is the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of identifiable net assets acquired in business combinations. We allocate goodwill to reporting units based on the reporting units that are expected to benefit from the business combination. We evaluate our reporting units on an annual basis. If necessary, we reassign goodwill using a relative fair value allocation approach.
We evaluate goodwill for impairment on an annual basis as of the last day of our third fiscal quarter, or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying value. These events or circumstances could include a significant change in the business climate, legal factors, operating performance indicators, competition, or sale or disposition of a significant portion of a reporting unit. We monitor the existence of potential impairment indicators throughout the fiscal year.
We test for goodwill impairment at the reporting unit level. We consider our service lines Labor Ready, Spartan Staffing, CLP Resources, PlaneTechs, and Centerline to be reporting units for goodwill impairment testing. In fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011, there were no changes to our reporting units. The impairment test involves comparing the fair value of each reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. Fair value reflects the price a market participant would be willing to pay in a potential sale of the reporting unit. If the fair value exceeds carrying value, then we conclude that no goodwill impairment has occurred. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, a second step is required to measure possible goodwill impairment loss. The second step includes hypothetically valuing the tangible and intangible assets and liabilities of the reporting unit as if the reporting unit had been acquired in a business combination. Then, the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill is compared to the carrying value of that goodwill. If the carrying value of the reporting unit’s goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of the goodwill, we recognize an impairment loss in an amount equal to the excess, not to exceed the carrying value.
Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions to evaluate the impact of operating and macroeconomic changes on each reporting unit. The fair value of each reporting unit is estimated using a discounted cash flow methodology. This analysis requires significant judgments, including estimation of future cash flows, which is dependent on internal forecasts, estimation of the long-term rate of growth for our business, estimation of the useful life over which cash flows will occur, and determination of our weighted average cost of capital, which is risk-adjusted to reflect the specific risk profile of the reporting unit being tested. Our weighted average cost of capital for our most recent impairment test ranged from 13% - 15%.
We also identify similar publicly traded companies and develop a correlation, referred to as a multiple, to apply to the operating results of the reporting units. The primary market multiples we compare to are revenue and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. These combined fair values are then reconciled to our aggregate market value of our shares of common stock on the date of valuation, while considering a reasonable control premium.
We base fair value estimates on assumptions we believe to be reasonable but that are unpredictable and inherently uncertain. Actual future results may differ from those estimates. Based on our test, all of our reporting units' fair values were significantly in excess of their carrying values, except PlaneTechs, and accordingly we have provided a sensitivity analysis for that reporting unit only.
We consider a reporting unit’s value to be substantially in excess of its fair value at 20% or greater. The annual impairment testing performed as of September 27, 2013, in accordance with ASC 350, “Intangibles - Goodwill and Other” (“Step One”) indicated that each of the reporting units, except PlaneTechs, had a fair value substantially in excess of its carrying value. The PlaneTechs reporting unit passed Step One of the goodwill impairment test, but does not have a fair value substantially in excess of its carrying value. The estimated fair value of the PlaneTechs reporting unit was in excess of its carrying value by approximately 19% as of the assessment date. The reporting unit, which was acquired in 2007, had a goodwill balance of $19.1 million as of September 27, 2013. In order to conclude upon the assumptions for the discounted cash flow analysis, we considered multiple factors, including (a) macroeconomic conditions, (b) industry and market factors such as competition and changes in the market for the reporting unit's temporary labor services, (c) overall financial performance such as cash flows, actual and planned revenue, and profitability, and (d) changes in strategy for the reporting unit to expand its service offerings. If the PlaneTechs reporting unit does not meet its projections it could become impaired. The assumption with the most impact on our determination of the estimated fair value of the PlaneTechs reporting unit is sales growth. A reduction in the annual revenue growth assumption by 3% and no corresponding change to the operating costs would result in an indicator of possible goodwill impairment.
The blue-collar staffing market is subject to volatility based on overall economic conditions. As a consequence, our revenues tend to increase quickly when the economy begins to grow. Conversely, our revenues also decrease quickly when the economy begins to weaken, as occurred during the most recent recession. If actual results were to significantly deviate from management's estimates and assumptions of future performance, we could experience a material impairment to our goodwill.
We have indefinite-lived intangible assets related to our CLP Resources and Spartan Staffing trade names. We test our trade names annually for impairment, or when indications of potential impairment exist. We utilize the relief from royalty method to determine the fair value of each of our trade names. If the carrying value exceeds the fair value, we recognize an impairment loss in an amount equal to the excess. Considerable management judgment is necessary to determine key assumptions, including projected revenue, royalty rates and appropriate discount rates. We performed our annual indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment test as of September 27, 2013 and determined that the estimated fair value exceeded the carrying amount. Accordingly, no impairment loss was required to be recognized during 2013.
An impairment assessment of physical assets is necessary whenever events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. In such cases, the asset must be written down to the greater of the net realizable value or fair market value.
Reserves for contingent legal and regulatory liabilities
From time to time we are subject to compliance audits by federal, state, and local authorities relating to a variety of regulations including wage and hour laws, taxes, workers’ compensation, immigration, and safety. We are also subject to legal proceedings in the ordinary course of our operations. We have established reserves for contingent legal and regulatory liabilities. We record a liability when our management judges that it is probable that a legal claim will result in an adverse outcome and the amount of liability can be reasonably estimated. To the extent that an insurance company is contractually obligated to reimburse us for a liability, we record a receivable for the amount of the probable reimbursement. We evaluate our reserve regularly throughout the year and make adjustments as needed. If the actual outcome of these matters is different than expected, an adjustment is charged or credited to expense in the period the outcome occurs or the period in which the estimate changes.
Income taxes and related valuation allowances
We account for income taxes by recording taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in our financial statements or tax returns. We measure these expected future tax consequences based upon the provisions of tax law as currently enacted; the effects of future changes in tax laws are not anticipated. Future tax law changes, such as changes to federal and state corporate tax rates and the mix of states and their taxable income, could have a material impact on our financial condition or results of operations. When appropriate, we record a valuation allowance against deferred tax assets to offset future tax benefits that may not be realized. In determining whether a valuation allowance is appropriate, we consider whether it is more likely than not that all or some portion of our deferred tax assets will not be realized, based in part upon management’s judgments regarding future events and past operating results.
NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
See Note 1 to our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| |
Item 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates, each of which could adversely affect the value of our investments. We do not currently use derivative financial instruments.
Interest Rate Risks
Our exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates relates primarily to our investment portfolio.
Trust Assets
Restricted cash and investments consist principally of collateral that has been provided or pledged to insurance carriers for workers' compensation and state workers' compensation programs. Our insurance carriers and certain state workers' compensation programs require us to collateralize a portion of the workers' compensation obligation. The collateral typically takes the form of cash and cash equivalents and highly rated investment grade securities, primarily in U.S Treasury securities, U.S. agency debentures, U.S. agency mortgages, corporate securities and municipal securities. The majority of our collateral obligations are held in a trust ("Trust") at the Bank of New York Mellon. The individual investments within the Trust are subject to credit risk due to possible rating changes, default or impairment. We monitor the portfolio to ensure this risk does not exceed prudent levels. We consistently apply and adhere to our investment policy of holding high quality, diversified securities. We have the positive intent and ability to hold these investments until maturity and accordingly have classified them as held-to-maturity. Any fluctuation or change in interest rates would not impact our net income. Furthermore, an increase or decrease in interest rates immediately and uniformly by 10% would not have a material effect on our restricted cash and investments or cash and cash equivalents balances.
Corporate Investments
Our available-for-sale securities are comprised of investments with original maturities greater than three months and are classified as marketable securities. Our marketable securities consist of CDs, VRDNs, and commercial paper. The primary objectives of these investments are to preserve capital and liquidity. Available-for-sale securities are recorded on the consolidated balance sheets at fair value with unrealized gains and losses reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income. We do not hedge the interest rate exposure on our available-for-sale securities. An increase or decrease in interest rates immediately and uniformly by 10% would not have a material effect on our available-for-sale securities balances.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
The majority of our revenue, expense, liabilities, and capital purchasing activities are transacted in U.S. dollars. However, because a portion of our operations consists of activities outside of the U.S., we have transactions in other currencies, primarily the Canadian dollar. We have not hedged our foreign currency translation risk. We have the ability to hold our foreign-currency denominated assets indefinitely and do not expect that a sudden or significant change in foreign exchange rates will have a material impact on future operating results or cash flows.
| |
Item 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
The following consolidated financial statements of the Company and its subsidiaries are included herein as indicated below:
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets - December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations & Comprehensive Income - Fiscal years ended December 27, 2013, December 28, 2012, and December 30, 2011 |
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity - Fiscal years ended December 27, 2013, December 28, 2012, and December 30, 2011 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - Fiscal years ended December 27, 2013, December 28, 2012, and December 30, 2011 |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
Selected Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of TrueBlue, Inc.
Tacoma, Washington
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of TrueBlue, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 27, 2013. Our audits also included the financial statement schedules listed in the Index at Item 15(a)(2). These financial statements and financial statement schedules are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and financial statement schedules based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of TrueBlue, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 27, 2013, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedules, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 27, 2013, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 20, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Seattle, Washington
February 20, 2014
TRUEBLUE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except par value data)
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27,
2013 | | December 28,
2012 |
ASSETS | | | |
Current assets: | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 122,003 |
| | $ | 129,513 |
|
Marketable securities | 14,745 |
|
| — |
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $5,710 and $4,999 | 199,519 |
| | 167,292 |
|
Prepaid expenses, deposits and other current assets | 9,491 |
| | 8,541 |
|
Income tax receivable | 3,060 |
| | 6,373 |
|
Deferred income taxes | 7,640 |
| | 5,447 |
|
Total current assets | 356,458 |
| | 317,166 |
|
Property and equipment, net | 54,473 |
| | 58,171 |
|
Restricted cash and investments | 154,558 |
| | 136,259 |
|
Deferred income taxes | 4,213 |
| | 2,562 |
|
Goodwill | 82,239 |
| | 48,079 |
|
Intangible assets, net | 31,505 |
| | 16,554 |
|
Other assets, net | 36,015 |
| | 22,952 |
|
Total assets | $ | 719,461 |
| | $ | 601,743 |
|
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | |
Accounts payable and other accrued expenses | $ | 29,850 |
| | $ | 27,292 |
|
Accrued wages and benefits | 39,094 |
| | 35,102 |
|
Current portion of workers' compensation claims reserve | 49,942 |
| | 44,652 |
|
Other current liabilities | 2,523 |
| | 6,510 |
|
Total current liabilities | 121,409 |
| | 113,556 |
|
Workers’ compensation claims reserve, less current portion | 164,887 |
| | 150,937 |
|
Note payable, less current portion | 29,656 |
| | — |
|
Other long-term liabilities | 10,149 |
| | 3,576 |
|
Total liabilities | 326,101 |
| | 268,069 |
|
| | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 9) |
| |
|
| | | |
Shareholders’ equity: | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.131 par value, 20,000 shares authorized; No shares issued and outstanding | — |
| | — |
|
Common stock, no par value, 100,000 shares authorized; 41,085 and 40,220 shares issued and outstanding | 1 |
| | 1 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income | 2,033 |
| | 2,818 |
|
Retained earnings | 391,326 |
| | 330,855 |
|
Total shareholders’ equity | 393,360 |
| | 333,674 |
|
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 719,461 |
| | $ | 601,743 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
TRUEBLUE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FISCAL YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 27, 2013, DECEMBER 28, 2012, AND DECEMBER 30, 2011
(in thousands, except per share data) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Revenue from services | $ | 1,668,929 |
| | $ | 1,389,530 |
| | $ | 1,316,013 |
|
Cost of services | 1,226,626 |
| | 1,017,145 |
| | 968,967 |
|
Gross profit | 442,303 |
| | 372,385 |
| | 347,046 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 362,248 |
| | 300,459 |
| | 282,828 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 20,472 |
| | 18,890 |
| | 16,384 |
|
Income from operations | 59,583 |
| | 53,036 |
| | 47,834 |
|
Interest expense | (1,248 | ) | | (1,131 | ) | | (1,207 | ) |
Interest and other income | 2,602 |
| | 2,700 |
| | 2,697 |
|
Interest and other income, net | 1,354 |
| | 1,569 |
| | 1,490 |
|
Income before tax expense | 60,937 |
| | 54,605 |
| | 49,324 |
|
Income tax expense | 16,013 |
| | 20,976 |
| | 18,533 |
|
Net income | $ | 44,924 |
| | $ | 33,629 |
| | $ | 30,791 |
|
| | | | | |
Net income per common share: | | | | | |
Basic | $ | 1.12 |
| | $ | 0.85 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
|
Diluted | $ | 1.11 |
| | $ | 0.84 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
|
Weighted average shares outstanding: | | | | | |
Basic | 40,166 |
| | 39,548 |
| | 41,961 |
|
Diluted | 40,502 |
| | 39,862 |
| | 42,322 |
|
| | | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of tax | $ | (689 | ) | | $ | 175 |
| | $ | (263 | ) |
Unrealized loss on investments, net of tax | (96 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | (785 | ) | | 175 |
| | (263 | ) |
Comprehensive income | $ | 44,139 |
| | $ | 33,804 |
| | $ | 30,528 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
TRUEBLUE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
FISCAL YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 27, 2013, DECEMBER 28, 2012, AND DECEMBER 30, 2011
(in thousands) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock | | Retained earnings | | Accumulated other comprehensive income | | Total shareholders' equity |
| Shares | | Amount | | | | | | |
Balances, December 31, 2010 | 44,086 |
| | $ | 1 |
| | $ | 309,800 |
| | $ | 2,906 |
| | $ | 312,707 |
|
Net income | | | | | 30,791 |
| | | | 30,791 |
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of tax | | | | | | | (263 | ) | | (263 | ) |
Purchases and retirement of common stock | (4,455 | ) | | | | (56,932 | ) | | | | (56,932 | ) |
Issuances under equity plans, including tax benefits | 302 |
| | | | (156 | ) | | | | (156 | ) |
Stock-based compensation | | | | | 7,432 |
| | | | 7,432 |
|
Balances, December 30, 2011 | 39,933 |
| | $ | 1 |
| | $ | 290,935 |
| | $ | 2,643 |
| | $ | 293,579 |
|
Net income | | | | | 33,629 |
| | | | 33,629 |
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of tax | | | | | | | 175 |
| | 175 |
|
Purchases and retirement of common stock | (306 | ) | | | | (4,386 | ) | | | | (4,386 | ) |
Issuances under equity plans, including tax benefits | 593 |
| | | | 2,760 |
| | | | 2,760 |
|
Stock-based compensation | | | | | 7,917 |
| | | | 7,917 |
|
Balances, December 28, 2012 | 40,220 |
| | $ | 1 |
| | $ | 330,855 |
| | $ | 2,818 |
| | $ | 333,674 |
|
Net income | | | | | 44,924 |
| | | | 44,924 |
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of tax | | | | | | | (689 | ) | | (689 | ) |
Unrealized loss on investments, net of tax | | | | | | | (96 | ) | | (96 | ) |
Issuances under equity plans, including tax benefits | 865 |
| | | | 7,135 |
| | | | 7,135 |
|
Stock-based compensation | | | | | 8,412 |
| | | | 8,412 |
|
Balances, December 27, 2013 | 41,085 |
| | $ | 1 |
| | $ | 391,326 |
| | $ | 2,033 |
| | $ | 393,360 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
TRUEBLUE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FISCAL YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 27, 2013, DECEMBER 28, 2012, AND DECEMBER 30, 2011
(in thousands) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
Net income | $ | 44,924 |
| | $ | 33,629 |
| | $ | 30,791 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash from operating activities: | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | 20,472 |
| | 18,890 |
| | 16,384 |
|
Provision for doubtful accounts | 12,063 |
| | 6,994 |
| | 6,638 |
|
Stock-based compensation | 8,412 |
| | 7,917 |
| | 7,432 |
|
Deferred income taxes | (3,844 | ) | | 3,091 |
| | (1,910 | ) |
Other operating activities | 2,116 |
| | 1,946 |
| | (473 | ) |
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | (4,181 | ) | | (20,408 | ) | | (51,824 | ) |
Income taxes | 4,113 |
| | (3,748 | ) | | 3,513 |
|
Other assets | (7,341 | ) | | (1,214 | ) | | (1,244 | ) |
Accounts payable and other accrued expenses | (3,592 | ) | | 1,524 |
| | 5,423 |
|
Accrued wages and benefits | (3,643 | ) | | (182 | ) | | 10,793 |
|
Workers’ compensation claims reserve | 9,859 |
| | 3,746 |
| | 4,537 |
|
Other liabilities | 6,710 |
| | 138 |
| | 529 |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities | 86,068 |
| | 52,323 |
| | 30,589 |
|
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
Capital expenditures | (13,003 | ) | | (17,826 | ) | | (9,707 | ) |
Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | (77,560 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Purchases of marketable securities | (40,800 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
Sales and maturities of marketable securities | 20,050 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | (16,122 | ) | | 7,587 |
| | 68,504 |
|
Purchases of restricted investments | (13,411 | ) | | (33,778 | ) | | (88,173 | ) |
Maturities of restricted investments | 15,581 |
| | 18,116 |
| | 9,238 |
|
Other | — |
| | (250 | ) | | (6,800 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | (125,265 | ) | | (26,151 | ) | | (26,938 | ) |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
Purchases and retirement of common stock | — |
| | (4,386 | ) | | (56,932 | ) |
Net proceeds from stock option exercises and employee stock purchase plans | 9,136 |
| | 4,164 |
| | 1,131 |
|
Common stock repurchases for taxes upon vesting of restricted stock | (2,800 | ) | | (2,154 | ) | | (1,776 | ) |
Proceeds from note payable | 34,000 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Payments on debt and other liabilities | (8,681 | ) | | (4,548 | ) | | (302 | ) |
Other | 713 |
| | 751 |
| | 664 |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 32,368 |
| | (6,173 | ) | | (57,215 | ) |
Effect of exchange rates on cash | (681 | ) | | 203 |
| | (278 | ) |
Net change in cash and cash equivalents | (7,510 | ) | | 20,202 |
| | (53,842 | ) |
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period | 129,513 |
| | 109,311 |
| | 163,153 |
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period | $ | 122,003 |
| | $ | 129,513 |
| | $ | 109,311 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| |
NOTE 1: | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Description of business
TrueBlue, Inc. (“TrueBlue,” “we,” “us,” “our”) is a leading provider of temporary blue-collar staffing services. We help over 130,000 businesses be more productive through easy access to dependable temporary labor. We provide a wide range of specialized blue-collar staffing services to industries that include construction, manufacturing, transportation, waste, hospitality, retail, energy, and many more. We operate as: Labor Ready for general labor, Spartan Staffing for light industrial, CLP Resources for skilled trades, PlaneTechs for aviation and diesel mechanics and technicians, and Centerline Drivers for dedicated and temporary drivers. We have a network of 757 branches in all 50 states, Puerto Rico and Canada. We also have customer on-site locations, which are generally dedicated to one customer, and national service centers that supply our customers with temporary workers.
We began operations in 1989 under the name Labor Ready, Inc. providing on-demand, general labor staffing services. We became a public company in 1995. In 2004 we began acquiring additional brands to expand our service offerings to customers in the blue-collar staffing market. Effective December 18, 2007, Labor Ready, Inc. changed its name to TrueBlue, Inc. We are headquartered in Tacoma, Washington.
Basis of presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of TrueBlue, Inc. and all of its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”).
Our TrueBlue service lines are our operating segments and are aggregated into one reportable segment in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Our operations are all in the blue-collar staffing market of the temporary staffing industry and supply customers with temporary workers. All our service lines have the following similar characteristics:
| |
• | They provide blue-collar temporary labor services; |
| |
• | They serve customers who have a need for temporary staff to perform tasks, which do not require a permanent employee; |
| |
• | They each build a temporary workforce through recruiting, screening, and hiring. Temporary workers are dispatched to customers where they work under the supervision of our customers; |
| |
• | They each drive profitability by managing the bill rates to our customers and the pay rates to our workers. Profitable growth is also driven by leveraging our cost structure across all service lines. |
Our long-term performance expectations of all our service lines are similar as are the underlying financial and economic metrics used to manage those service lines.
Our international operations are not significant to our total operations for segment reporting purposes. Total revenues from our international operations were 3.1%, 3.5%, and 3.8% of our total revenues for fiscal years ending 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
Fiscal year end
Our fiscal year ends on the last Friday of December.
Revenue recognition
Revenue from temporary staffing services is recognized at the time the service is provided and is net of adjustments related to customer credits. Revenue also includes billable travel and other reimbursable costs. Customer discounts or other incentives are recognized in the period the related revenue is earned. We discontinued the use of all domestic cash dispensing machines in fiscal 2012. Revenues are reported net of sales, use, or other transaction taxes collected from customers and remitted to taxing authorities.
We record revenue on a gross basis as a principal versus on a net basis as an agent in the consolidated statement of operations. We have determined that gross reporting as a principal is the appropriate treatment based upon the following key factors:
| |
• | We maintain the direct contractual relationship with the customer. |
| |
• | We have discretion in selecting and assigning the temporary workers to particular jobs and establishing their billing rate. |
| |
• | We bear the risk and rewards of the transaction including credit risk if the customer fails to pay for services performed. |
Cost of services
Cost of services primarily includes wages of temporary workers and related payroll taxes and workers’ compensation expenses. Cost of services also includes billable travel and other reimbursable costs.
Advertising costs
Advertising costs consist primarily of print and other promotional activities. We expense advertisements as of the first date the advertisements take place. Advertising expenses included in selling, general and administrative expenses were $4.0 million, $3.7 million, and $3.6 million in 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
Cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities
We consider all highly liquid instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less at date of purchase to be cash equivalents. Investments with original maturities greater than three months are classified as marketable securities. Our marketable securities consist of certificates of deposit ("CDs"), variable-rate demand notes ("VRDNs"), and commercial paper. All of our marketable securities are classified as available-for-sale and are reported at fair value, with any unrealized gains and losses, net of tax, recorded in Other comprehensive income (loss). We do not buy and hold securities principally for the purpose of selling them in the near future. Our investment policy is focused on the preservation of capital, liquidity and return. From time to time, we may sell certain securities but the objectives are generally not to generate profits on short-term differences in price. We manage our cash equivalents and marketable securities as a single portfolio of highly liquid securities.
Accounts receivable and allowance for doubtful accounts
Accounts receivable are recorded at the invoiced amount together with interest for certain past due accounts. We establish an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the failure of our customers to make required payments. The allowance for doubtful accounts is determined based on current collection efforts, historical collection trends, write-off experience, customer credit risk, and current economic data. The allowance for doubtful accounts is reviewed quarterly and represents our best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses. Past due balances are written-off when it is probable the receivable will not be collected. Our allowance for doubtful accounts was $5.7 million and $5.0 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively.
Restricted cash and investments
Cash and investments pledged as collateral and restricted to use for workers' compensation insurance programs are included as restricted cash and investments on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. Our investments consist of highly rated investment grade debt securities which are rated A or higher by nationally recognized statistical rating organizations. We have the positive intent and ability to hold all these investments until maturity in accordance with our investment policy and accordingly all of our investments are classified as held-to-maturity. In the event that an investment is downgraded, it is replaced with a highly rated investment grade security. We review for impairment on a quarterly basis and do not consider temporary unrealized losses to be impaired.
In 2011, we entered into an agreement with AIG and the Bank of New York Mellon creating a trust ("Trust"), which holds the majority of our collateral obligations under existing workers' compensation insurance policies. Placing the collateral in the Trust allows us to manage the investment of the assets and provides greater protection of those assets.
Fair value of financial instruments and investments
The carrying value of cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash approximates fair value because of the short-term maturity of those instruments. The fair value of our restricted investments is based upon the quoted market price on the last business day of the fiscal reporting period. Where an observable quoted market price for a security does not exist, we estimate fair value using a variety of valuation methodologies, which include observable inputs for comparable instruments and unobservable inputs. There are inherent limitations when estimating the fair value of financial instruments and the fair values reported are not necessarily indicative of the amounts that would be realized in current market transactions.
Property and equipment
Property and equipment are recorded at cost. We compute depreciation using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets.
|
| |
| Years |
Buildings | 40 |
Computers and software | 3 - 10 |
Furniture and equipment | 3 - 10 |
Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the related non-cancelable lease term, which is typically 90 days, or their estimated useful lives.
Non-capital expenditures associated with opening new branch locations are expensed as incurred.
When property is retired or otherwise disposed of, the cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss, net of proceeds, is reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Operations & Comprehensive Income.
Repairs and maintenance costs are charged directly to expense as incurred. Major renewals or replacements that substantially extend the useful life of an asset are capitalized and depreciated.
Costs associated with the acquisition or development of software for internal use are capitalized and amortized over the expected useful life of the software, from three to ten years. A subsequent addition, modification, or upgrade to internal-use software is capitalized to the extent that it enhances the software's functionality or extends its useful life. Software maintenance and training costs are expensed in the period incurred.
Leases
We conduct our branch office operations from leased locations. The leases require payment of real estate taxes, insurance and common area maintenance, in addition to rent. The terms of our lease agreements generally range from three to five years with options to cancel with 90 day notification. Most of the leases contain renewal options and escalation clauses.
For leases that contain predetermined fixed escalations of the minimum rent, we recognize the related rent expense on a straight-line basis from the date we take possession of the property to the end of the minimum lease term. We record any difference between the straight-line rent amounts and amounts payable under the leases as part of deferred rent, in accrued liabilities or long-term liabilities, as appropriate.
Cash or lease incentives received upon entering into certain branch leases ("tenant allowances") are recognized on a straight-line basis as a reduction to rent from the date we take possession of the property through the end of the initial lease term. We record the unamortized portion of tenant allowances as a part of deferred rent, in accrued liabilities or long-term liabilities, as appropriate.
Goodwill and intangible assets
Goodwill is the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of identifiable net assets acquired in business combinations. We allocated goodwill to reporting units based on the reporting units that are expected to benefit from the business combination. We do not amortize goodwill but test it for impairment annually as of the last day of our fiscal third quarter, or when indications of potential impairment exist. We monitor the existence of potential impairment indicators throughout the fiscal year.
We test for goodwill impairment at the reporting unit level. We consider our service lines; Labor Ready, Spartan Staffing, CLP Resources, PlaneTechs and Centerline; to be reporting units for goodwill impairment testing. In fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011, there were no changes to our reporting units.
The impairment test involves comparing the fair value of each reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. Fair value reflects the price a market participant would be willing to pay in a potential sale of the reporting unit. If the fair value exceeds carrying value, then we conclude that no goodwill impairment has occurred. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, a second step is required to measure possible goodwill impairment loss. The second step includes hypothetically valuing the tangible and intangible assets and liabilities of the reporting unit as if the reporting unit had been acquired in a business combination. Then, the implied fair value of the reporting unit's goodwill is compared to the carrying value of that goodwill. If the carrying value of the reporting unit's goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of the goodwill, we recognize an impairment loss in an amount equal to the excess, not to exceed the carrying value.
Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions to evaluate the impact of operating and macroeconomic changes on each reporting unit. The fair value of each reporting unit is estimated using a discounted cash flow methodology. This analysis requires significant judgments, including estimation of future cash flows, which is dependent on internal forecasts, estimation of the long-term rate of growth for our business, estimation of the useful life over which cash flows will occur, and determination of our weighted average cost of capital, which is risk-adjusted to reflect the specific risk profile of the reporting unit being tested. We also identify similar publicly traded companies and develop a correlation, referred to as a multiple, to apply to the operating results of the reporting units. The primary market multiples we compare to are revenue and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. These combined fair values are then reconciled to our aggregate market value of our shares of common stock on the date of valuation, while considering a reasonable control premium. We base fair value estimates on assumptions we believe to be reasonable but that are unpredictable and inherently uncertain. Actual future results may differ from those estimates.
The blue-collar staffing market is subject to volatility based on overall economic conditions. As a consequence, our revenues tend to increase quickly when the economy begins to grow. Conversely, our revenues also decrease quickly when the economy begins to weaken, as occurred during the most recent recession. If actual results were to significantly deviate from management's estimates and assumptions of future performance, we could experience a material impairment to our goodwill.
We have indefinite-lived intangible assets related to our CLP Resources and Spartan Staffing trade names. We test our indefinite-lived intangible assets annually for impairment, or when indications of potential impairment exist. We utilize the relief from royalty method to determine the fair value of each of our trade names. If the carrying value exceeds the fair value, we recognize an impairment loss in an amount equal to the excess. Considerable management judgment is necessary to determine key assumptions, including projected revenue, royalty rates, and appropriate discount rates.
Long-lived asset impairment
Long-lived assets include property and equipment and definite-lived intangible assets. Definite-lived intangible assets consist of customer relationships, trade names and non-compete agreements. Long-lived assets are tested for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. Factors considered important that could result in an impairment review include, but are not limited to, significant under performance relative to historical or planned operating results, significant changes in the manner of use of the assets or significant changes in our business strategies. Long-lived assets are grouped at the lowest level at which identifiable cash flows are largely independent when assessing impairment. Our branch assets, including property and equipment, and customer relationship intangibles, are grouped and evaluated at the individual branch level. All other property and equipment and definite-lived intangibles are grouped at either the service line or corporate level as appropriate based on the identifiable cash flows. An impairment loss is recognized when the estimated undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset plus net proceeds expected from disposition of the asset (if any) are less than the carrying value of the asset. When an impairment loss is recognized, the carrying amount of the asset is reduced to its estimated fair value based on quoted market prices or other valuation techniques (e.g., discounted cash flow analysis). Considerable management judgment is necessary to estimate future after-tax cash flows, including cash flows from continuing use and terminal value. Accordingly, actual future results could vary from our estimates.
Branch closures and exit costs
We routinely evaluate our branch network and close under-performing branches. We classify closed branches in discontinued operations when the operations and cash flows of the branch have been or will be eliminated from ongoing operations. To determine if cash flows have been or will be eliminated from ongoing operations, we evaluate a number of qualitative and quantitative factors, including, but not limited to, proximity to remaining open branches and estimates of revenue migration from the closed branch to any branch remaining open. The estimated revenue migration is based on historical estimates of our revenue migration upon opening or closing a branch in a similar market. Branch closings meeting the criteria for discontinued operations were not material, individually or cumulatively, for any reporting year presented. Assets related to planned branch closures or other exit activities are evaluated for impairment in accordance with our impairment policy, giving consideration to revised estimates of future cash flows.
Workers’ compensation reserves
We maintain reserves for workers’ compensation claims using actuarial estimates of the future cost of claims and related expenses. These estimates include claims that have been reported but not settled and claims that have been incurred but not reported. These reserves, which reflect potential liabilities to be paid in future periods based on estimated payment patterns, are discounted to estimated net present value using discount rates based on average returns of “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments, which are evaluated on a quarterly basis. We evaluate the reserves regularly throughout the year and make adjustments accordingly. If the actual cost of such claims and related expenses exceed the amounts estimated, additional reserves may be required. Changes in
reserve estimates are reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Operations & Comprehensive Income in the period when the changes in estimates are made.
Our workers’ compensation reserves include estimated expenses related to claims above our self-insured limits (“excess claims”) and a corresponding receivable for the insurance coverage on excess claims based on the contractual policy agreements we have with insurance companies. We discount the liability and its corresponding receivable to its estimated net present value using the “risk-free” rates associated with the actuarially determined weighted average lives of our excess claims. When appropriate, based on our best estimate, we record a valuation allowance against the insurance receivable to reflect amounts that may not be realized.
Reserves for contingent legal and regulatory liabilities
From time to time we are subject to compliance audits by federal, state and local authorities relating to a variety of regulations including wage and hour laws, taxes, workers’ compensation, immigration, and safety. From time to time we are also subject to legal proceedings in the ordinary course of our operations. We establish reserves for contingent legal and regulatory liabilities when our management determines that it is probable that a legal claim will result in an adverse outcome and the amount of liability can be reasonably estimated. To the extent that an insurance company is contractually obligated to reimburse us for a liability, we record a receivable for the amount of the probable reimbursement. We evaluate our reserve regularly throughout the year and make adjustments as needed. If the actual outcome of these matters is different than expected, an adjustment is charged or credited to expense in the period the outcome occurs or the period in which the estimate changes.
Income taxes and related valuation allowance
We account for income taxes by recording taxes payable or receivable for the current year and deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in our financial statements or tax returns. These expected future tax consequences are measured based on provisions of tax law as currently enacted; the effects of future changes in tax laws are not anticipated. Future tax law changes, such as changes to the federal and state corporate tax rates and the mix of states and their taxable income, could have a material impact on our financial condition or results of operations. When appropriate, we record a valuation allowance against deferred tax assets to offset future tax benefits that may not be realized. In determining whether a valuation allowance is appropriate, we consider whether it is more likely than not that all or some portion of our deferred tax assets will not be realized, based in part upon management’s judgments regarding future events and past operating results. Based on that analysis, we have determined that a valuation allowance is appropriate for certain foreign net operating losses and state tax credits that we expect will not be utilized within the permitted carry forward periods as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012.
Stock-based compensation
Under various plans, officers, employees and non-employee directors have received or may receive grants of stock, restricted stock awards, performance share units, or options to purchase common stock. We also have an employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”).
Compensation expense for restricted stock awards and performance share units is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period, based on the stock’s fair market value on the grant date. For restricted stock grants issued with performance conditions, compensation expense is recognized over each vesting period based on assessment of the likelihood of meeting these conditions. We recognize compensation expense for only the portion of restricted stock and performance share units that is expected to vest, rather than record forfeitures when they occur. If the actual number of forfeitures differs from those estimated by management, additional adjustments to compensation expense may be required in the future periods. We determine the fair value of options to purchase common stock using the Black-Scholes valuation model, which requires the input of subjective assumptions. We recognize expense over the service period for options that are expected to vest and record adjustments to compensation expense at the end of the service period if actual forfeitures differ from original estimates.
Foreign currency
Cumulative foreign currency translation adjustments relate to our consolidated foreign subsidiary. Assets and liabilities recorded in foreign currencies are translated at the applicable exchange rate on the balance sheet date. Revenue and expenses are translated at average rates of exchange prevailing during the year.
Purchases and retirement of our common stock
Purchases of our common stock are not displayed separately as treasury stock on the Consolidated Balance Sheets in accordance with the Washington Business Corporation Act, which requires the retirement of purchased shares. As a result, shares of our common stock that we purchase are retired immediately. It is our accounting policy to first record these purchases as a reduction to our common stock account. Once the common stock account has been reduced to a nominal balance, remaining purchases are recorded as a reduction to our Retained earnings account. Furthermore, activity in our common stock account related to stock-
based compensation is also recorded to Retained earnings until such time as the reduction to Retained earnings due to stock repurchases has been recovered.
Shares outstanding
Shares outstanding include shares of unvested restricted stock. Unvested restricted stock included in reportable shares outstanding was 0.7 million and 0.6 million shares as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. Shares of unvested restricted stock are excluded from our calculation of basic weighted average shares outstanding, but their dilutive impact is added back in the calculation of diluted weighted average shares outstanding.
Use of estimates
Preparing financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses. Examples include, but are not limited to, allowance for doubtful accounts, estimates for asset and goodwill impairments, stock-based performance awards, assumptions underlying self-insurance reserves, and the potential outcome of future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the financial statements. Actual results and outcomes may differ from these estimates and assumptions.
Recently issued accounting pronouncements not yet adopted
In July 2013, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for the presentation of an unrecognized tax benefit when a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward exists. The guidance requires that an unrecognized tax benefit, or a portion of an unrecognized tax benefit, be presented in the financial statements as a reduction to a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward, except to the extent when, for certain reasons, it is not available. The guidance will be effective for our first quarter of fiscal 2014. Management does not expect the adoption of this guidance to have a material impact on our financial statements.
We account for our business acquisitions using the purchase method of accounting. The fair value of the net assets acquired and the results of the acquired business are included in the financial statements from the acquisition date forward. We are required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and results of operations during the reporting period. Estimates are used in accounting for, among other things, the fair value of acquired net operating assets, property and equipment, intangible assets, useful lives of property and equipment and amortizable lives for acquired intangible assets. Any excess of the purchase consideration over the identified fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed is recognized as goodwill. All acquisition related costs are expensed as incurred and recorded in operating expenses. Additionally, we recognize liabilities for anticipated restructuring costs that will be necessary due to the elimination of excess capacity, redundant assets, or unnecessary functions and record them as operating expenses. We estimate the preliminary fair value of acquired assets and liabilities as of the date of acquisition based on information available at that time. The valuation of these tangible and identifiable intangible assets and liabilities is subject to further management review and may change between the preliminary allocation and the final allocation. Any changes to these estimates may have a material impact on our operating results or financial condition. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the net assets acquired was recorded as goodwill and are entirely deductible for tax purposes.
MDT Personnel, LLC
Effective February 4, 2013, we acquired substantially all of the assets and assumed certain liabilities of MDT Personnel, LLC and its subsidiaries ("MDT") for $53.4 million in cash. Assets acquired included finite-lived intangible assets of $10.2 million. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the net assets acquired in the amount of $25.7 million was recorded as goodwill and primarily represents synergies with our existing business, the acquired assembled workforce, and potential new customers. Through its network of 105 branches in 25 states, MDT supplied blue-collar labor to industries similar to those served by TrueBlue, including construction, event staffing, disaster recovery, hospitality, and manufacturing.
We incurred acquisition and integration-related costs of $6.0 million.We have fully integrated and blended MDT's operations with our existing service lines. MDT was primarily integrated into the Labor Ready service line. The integration of the MDT sales and branch operations was completed during the first quarter of 2013. We consolidated 65 branches, blended our sales and service teams and fully integrated all former MDT locations into our enterprise systems to optimize our combined operational efficiencies during the first quarter of 2013. We completed the integration of all remaining administrative services during the second quarter of 2013. These activities consisted of integrating our branch network capacity, sales and services teams and infrastructure and included closing, consolidating and relocating certain branch offices and administrative operations, eliminating redundant assets,
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
and reducing excess administrative workforce and capacity. These integration costs are included in Selling, general and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income and Cash flows from operating activities in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the year ended December 27, 2013.
Purchase price allocation
The following table summarizes the final allocation of the MDT purchase price, based on the estimated fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date of February 4, 2013 (in millions):
|
| | | | |
| | Purchase Price Allocation |
Cash | | $ | 0.4 |
|
Accounts receivable (1) | | 29.9 |
|
Prepaid expenses, deposits and other current assets | | 0.6 |
|
Property and equipment | | 0.3 |
|
Restricted cash | | 6.9 |
|
Intangible assets | | 10.2 |
|
Total assets acquired | | 48.3 |
|
| | |
Accounts payable and other accrued expenses | | 6.3 |
|
Accrued wages and benefits | | 4.8 |
|
Workers' compensation claims reserve | | 9.4 |
|
Other long-term liabilities | | 0.1 |
|
Total liabilities assumed | | 20.6 |
|
| | |
Net identifiable assets acquired | | 27.7 |
|
Goodwill | | 25.7 |
|
Net assets acquired | | $ | 53.4 |
|
| |
(1) | The gross contractual amount of accounts receivable was $32.9 million of which $3.0 million was estimated to be uncollectible. |
Intangible assets include identifiable intangible assets for customer relationships, the trade name/trademarks and a non-compete agreement. We estimated the fair value of the acquired identifiable intangible assets, which are subject to amortization using the income approach. No residual value is estimated for any of the intangible assets. The following table sets forth the components of identifiable intangible assets and their estimated useful lives as of February 4, 2013 (in millions, except for estimated useful lives, in years):
|
| | | | | |
| Estimated Fair Value | | Estimated Useful Life |
Customer relationships | $ | 7.8 |
| | 8.0 |
Trade name/trademarks | $ | 1.0 |
| | 1.5 |
Non-compete agreement | $ | 1.4 |
| | 5.0 |
The acquired assets and liabilities of MDT are included in our Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 27, 2013 and the results of its operations and cash flows are reported in our Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income and Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows from February 4, 2013.
MDT operations have been fully integrated with our existing operations and our customers, temporary workforce, field employees, and locations have been merged. The nature of the customers and the services provided by TrueBlue and the former MDT are substantially the same. We competed in the marketplace for the same customers, temporary workers, and sales and service personnel. Accordingly, subsequent to merging our operations, it is not possible to segregate and to accurately estimate the revenues and expenses related exclusively to the former MDT operations.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
Pro forma financial information (unaudited)
The following table reflects the pro forma consolidated results of operations for the periods presented, as though the acquisition of MDT had occurred as of the beginning of the period being reported on, after giving effect to related income taxes.
The pro forma financial information combines our results of operations with the unaudited financial information of MDT used by MDT management for internal reporting purposes. Any changes required by an audit of the MDT financial information could be material. The unaudited pro forma financial information presented is for illustrative purposes only and is not indicative of the results of operations that would have been realized if the acquisition had been completed on the dates indicated, nor is it indicative of future operating results.
The unaudited pro forma consolidated results of operations do not include, among other items, the effects of potential losses in gross profit due to revenue attrition from combining the two companies, and differences in our operating costs structure. It does include differences in workers' compensation and certain payroll taxes for temporary employees, and amortization of finite-lived intangible assets. 2013 pro forma net income was adjusted to exclude $6.0 million of acquisition and integration-related costs incurred in 2013. 2012 pro forma earnings were adjusted to include these charges.
Pro forma financial data (unaudited) is presented below (in millions, except per share data).
|
| | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 |
Revenue from services | $ | 1,693.1 |
| | $ | 1,612.5 |
|
Net income | $ | 49.0 |
| | $ | 25.9 |
|
Net income per common share - diluted | $ | 1.21 |
| | $ | 0.65 |
|
The Work Connection, Inc.
Effective October 1, 2013, we acquired certain assets and liabilities of The Work Connection, Inc. ("TWC"). TWC was founded in 1986 and provided light industrial services out of 37 branches in nine states. This acquisition provides us geographic expansion into new markets for our Spartan Staffing service line. TWC’s operations were integrated with those of our Spartan Staffing service line during the fourth quarter ended December 27, 2013. The acquisition of TWC was not material individually or in the aggregate to our consolidated results of operations and as such, pro forma financial statements were not required. The total cost of the acquisition was $22.7 million. We incurred acquisition and integration-related costs of $1.2 million for the purchase of TWC. Assets acquired included finite-lived intangible assets of $8.2 million. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the net assets acquired in the amount of $7.6 million was recorded as goodwill and primarily represents synergies with our existing business, acquired assembled workforce, and potential new customers.
The following table summarizes the final allocation of the TWC purchase price, based on the estimated fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date of October 1, 2013 (in millions):
|
| | | | |
| | Purchase Price Allocation |
Accounts receivable (1) | | $ | 10.2 |
|
Plant and equipment | | 0.2 |
|
Intangible assets | | 8.2 |
|
Total assets acquired | | 18.6 |
|
| | |
Accounts payable | | 0.6 |
|
Accrued wages and benefits | | 2.9 |
|
Total liabilities assumed | | 3.5 |
|
| | |
Net identifiable assets acquired | | 15.1 |
|
Goodwill | | 7.6 |
|
Net assets acquired | | $ | 22.7 |
|
| |
(1) | The gross contractual amount of accounts receivable was $10.4 million of which $0.2 million was estimated to be uncollectible. |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
Other immaterial acquisition
We acquired certain assets of Crowley Transportation Services, LLC ("CTS") in June 2013. The total cost of the acquisition was $2.4 million, including contingent consideration of $0.6 million. The acquisition of CTS was not material individually or in the aggregate to our consolidated results of operations and as such, pro forma financial statements were not required.
See Note 7 to the consolidated financial statements for further discussion of goodwill and intangible assets acquired during 2013.
| |
NOTE 3: | FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT |
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. We apply a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value:
| |
• | Level 1 inputs are valued using quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Our Level 1 assets primarily include cash and cash equivalents and mutual funds. |
| |
• | Level 2 inputs are valued based upon quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets or quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active. Our Level 2 assets are marketable securities, which primarily consist of CDs, VRDNs, commercial paper, and restricted investments, which primarily consist of municipal debt-securities, corporate-debt securities, asset-backed securities, and U.S. agency debentures. Our investments consist of highly rated investment grade debt securities which are rated A- or higher by nationally recognized statistical rating organizations. We obtain our inputs from quoted market prices and independent pricing vendors. |
| |
• | Level 3 inputs are generally unobservable and typically reflect management's estimates of assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. We currently have no Level 3 assets or liabilities. |
The carrying value of our accounts receivable and accounts payable approximates fair value due to their short-term nature. We also hold certain restricted investments, which collateralize workers' compensation programs and are classified as held-to-maturity and carried at amortized cost on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The following tables present the fair value and hierarchy for our financial assets (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 |
| Carrying Value | | Total Fair Value | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents (1) | $ | 122.0 |
| | $ | 122.0 |
| | $ | 122.0 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
Marketable securities classified as available-for-sale (2) | 20.7 |
| | 20.7 |
| | — |
| | 20.7 |
| | — |
|
Restricted cash and cash equivalents (1) | 57.1 |
| | 57.1 |
| | 57.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Other restricted assets (3) | 10.8 |
| | 10.8 |
| | 10.8 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Restricted investments classified as held-to-maturity (4) | 86.7 |
| | 86.9 |
| | — |
| | 86.9 |
| | — |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 28, 2012 |
| Carrying Value | | Total Fair Value | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents (1) | $ | 129.5 |
| | $ | 129.5 |
| | $ | 129.5 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
Restricted cash and cash equivalents (1) | 38.1 |
| | 38.1 |
| | 38.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Other restricted assets (3) | 7.0 |
| | 7.0 |
| | 7.0 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Restricted investments classified as held-to-maturity (4) | 91.2 |
| | 92.7 |
| | — |
| | 92.7 |
| | — |
|
| |
(1) | Cash equivalents and restricted cash equivalents consist of money market funds, deposits, and investments with original maturities of three months or less. |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
| |
(2) | Marketable securities include CDs, VRDNs, and commercial paper, which are classified as available-for-sale. Our CDs include $6.0 million with maturities greater than one year and are classified as Other assets on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. VRDNs with contractual maturities beyond one year are classified as short-term based on their highly liquid nature and because they represent the investment of cash that is available for current operations. Despite the long-term nature of their stated contractual maturities, we routinely buy and sell these securities and believe we have the ability to quickly sell them to the re-marketing agent at par value plus accrued interest in the event we decide to liquidate our investment in a particular VRDN. |
| |
(3) | Primarily consists of restricted cash in money market accounts and deferred compensation plan accounts, which are comprised of mutual funds. |
| |
(4) | Restricted investments classified as held-to-maturity consist of highly rated investment grade securities, primarily in municipal-debt securities, corporate-debt securities, asset-backed securities, and U.S. agency debentures. |
| |
NOTE 4. | MARKETABLE SECURITIES |
Marketable securities consist of CDs, VRDNs, and commercial paper, which are classified as available-for-sale. VRDNs are long-term municipal and corporate securities with an interest rate that is reset frequently. All of the VRDNs currently in our portfolio are backed by a bank Letter of Credit. Our VRDNs may be tendered at any time with a typical settlement date of less than one week. We did not hold any marketable securities at December 28, 2012.
The following table presents the amortized cost and fair value of our available-for-sale investments, which are carried at fair value (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 |
| Amortized Cost | | Fair Value |
Certificates of deposit | $ | 10.0 |
| | $ | 9.9 |
|
Variable-rate demand notes | 5.8 |
| | 5.8 |
|
Commercial paper | 5.0 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| $ | 20.8 |
| | $ | 20.7 |
|
Gross unrealized gains and loss were de minimis for the year ended December 27, 2013. We held no available-for-sale securities during the year ended December 28, 2012. Our marketable securities have not resulted in any other-than-temporary impairments for the year ended December 27, 2013.
The amortized cost and fair value by contractual maturity of our available-for-sale investments are as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 |
| Amortized Cost | | Fair Value |
Due in one year or less (1) | $ | 14.8 |
| | $ | 14.7 |
|
Due after one year (2) | 6.0 |
| | 6.0 |
|
| $ | 20.8 |
| | $ | 20.7 |
|
| |
(1) | Amounts due in one year or less include CDs, VRDNs, and commercial paper. The VRDNs have contractual terms ranging from two to 19 years. Although these securities are issued as long-term securities, they are priced and traded as short-term instruments because of the high liquidity provided through the tender feature. It is not our intent to hold to maturity. |
| |
(2) | Amounts due after one year include CDs with maturities between one and two years and are recorded in Other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. |
| |
NOTE 5: | RESTRICTED CASH AND INVESTMENTS |
Restricted cash and investments consist principally of collateral that has been provided or pledged to insurance carriers for workers' compensation and state workers' compensation programs. Our insurance carriers and certain state workers' compensation programs require us to collateralize a portion of our workers' compensation obligation. The collateral typically takes the form of cash and cash equivalents and highly rated investment grade securities, primarily in municipal-debt securities, corporate-debt securities, asset-backed securities, and U.S. agency debentures. Our investments have not resulted in any other-than-temporary impairments.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
The following is a summary of restricted cash and investments (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27,
2013 | | December 28,
2012 |
Cash collateral held by insurance carriers | $ | 23.7 |
| | $ | 21.5 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents held in Trust (1) | 31.5 |
| | 14.8 |
|
Investments held in Trust | 86.7 |
| | 91.2 |
|
Cash collateral backing letters of credit | 1.9 |
| | 1.8 |
|
Other (2) | 10.8 |
| | 7.0 |
|
Total restricted cash and investments | $ | 154.6 |
| | $ | 136.3 |
|
| |
(1) | Included in this amount is $0.8 million and $0.9 million of accrued interest at December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. |
| |
(2) | Primarily consists of restricted cash in money market accounts and deferred compensation plan accounts which are comprised of mutual funds. |
The following tables present fair value disclosures for our held-to-maturity investments, which are carried at amortized cost (in millions): |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 |
| Amortized Cost | | Gross Unrealized Gain | | Gross Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value |
Municipal debt securities | $ | 54.1 |
| | $ | 0.7 |
| | $ | (0.4 | ) | | $ | 54.4 |
|
Corporate debt securities | 19.7 |
| | 0.2 |
| | (0.3 | ) | | 19.6 |
|
Asset-backed securities | 12.9 |
| | 0.1 |
| | (0.1 | ) | | 12.9 |
|
| $ | 86.7 |
| | $ | 1.0 |
| | $ | (0.8 | ) | | $ | 86.9 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 28, 2012 |
| Amortized Cost | | Gross Unrealized Gain | | Gross Unrealized Loss | | Fair Value |
Municipal debt securities | $ | 57.3 |
| | $ | 1.0 |
| | $ | (0.1 | ) | | $ | 58.2 |
|
Corporate debt securities | 17.9 |
| | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | 18.2 |
|
Asset-backed securities | 16.0 |
| | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | 16.3 |
|
| $ | 91.2 |
| | $ | 1.6 |
| | $ | (0.1 | ) | | $ | 92.7 |
|
The amortized cost and fair value by contractual maturity of our held-to-maturity investments are as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 |
| Amortized Cost | | Fair Value |
Due in one year or less | $ | 10.2 |
| | $ | 10.2 |
|
Due after one year through five years | 42.1 |
| | 42.8 |
|
Due after five years through ten years | 34.4 |
| | 33.9 |
|
| $ | 86.7 |
| | $ | 86.9 |
|
Actual maturities may differ from contractual maturities because the issuers of certain debt securities have the right to call or prepay their obligations without penalty.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
| |
NOTE 6: | PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
Property and equipment are stated at cost and consist of the following (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27,
2013 | | December 28,
2012 |
Buildings and land | $ | 27.0 |
| | $ | 25.9 |
|
Computers and software | 101.9 |
| | 91.7 |
|
Cash dispensing machines | 1.0 |
| | 1.0 |
|
Furniture and equipment | 9.4 |
| | 8.9 |
|
Construction in progress | 2.9 |
| | 7.7 |
|
| 142.2 |
| | 135.2 |
|
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (87.7 | ) | | (77.0 | ) |
| $ | 54.5 |
| | $ | 58.2 |
|
Capitalized software costs, net of accumulated amortization, were $30.6 million and $30.9 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively, excluding amounts in Construction in progress. Construction in progress consists primarily of purchased and internally developed software.
Depreciation expense of property and equipment totaled $15.5 million, $15.8 million, and $13.5 million for 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
| |
NOTE 7: | GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
Goodwill
The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill were as follows (in millions):
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Goodwill | | Accumulated Impairment Losses | | Goodwill |
Balance at December 28, 2012 | $ | 94.3 |
| | $ | (46.2 | ) | | $ | 48.1 |
|
Goodwill acquired year to date (1) | 34.1 |
| | — |
| | 34.1 |
|
Balance at December 27, 2013 | $ | 128.4 |
|
| $ | (46.2 | ) | | $ | 82.2 |
|
| |
(1) | Goodwill acquired includes $25.7 million, $0.8 million, and $7.6 million due to the acquisitions of MDT, CTS, and TWC, respectively. |
Intangible assets
The following table presents our purchased finite-lived intangible assets (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 | | December 28, 2012 |
| Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Amount | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Amount |
Finite-lived intangible assets (1): | | | | | | | | | | | |
Customer relationships | $ | 35.9 |
| | $ | (13.9 | ) | | $ | 22.0 |
| | $ | 19.1 |
| | $ | (10.5 | ) | | $ | 8.6 |
|
Trade name/trademarks | 5.2 |
| | (2.7 | ) | | 2.5 |
| | 3.5 |
| | (1.6 | ) | | 1.9 |
|
Non-compete agreements | 1.8 |
| | (0.5 | ) | | 1.3 |
| | 1.8 |
| | (1.4 | ) | | 0.4 |
|
Total finite-lived intangible assets | $ | 42.9 |
| | $ | (17.1 | ) | | $ | 25.8 |
| | $ | 24.4 |
| | $ | (13.5 | ) | | $ | 10.9 |
|
| |
(1) | Excludes assets that are fully amortized. |
The components of intangible assets acquired for the fiscal year ended December 27, 2013, were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | MDT | | CTS | | TWC | | Total Acquired Intangible Assets | | Weighted Average Life |
Customer relationships | | $ | 7.8 |
| | $ | 1.4 |
| | $ | 7.6 |
| | $ | 16.8 |
| | 8 |
Trade name/trademarks | | 1.0 |
| | 0.1 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 1.7 |
| | 1 |
Non-compete agreements | | 1.4 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1.4 |
| | 5 |
Total intangible assets acquired | | $ | 10.2 |
| | $ | 1.5 |
| | $ | 8.2 |
| | $ | 19.9 |
| | |
Intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives. Amortization of our finite-lived intangible assets was $4.9 million, $3.1 million, and $2.9 million for 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
The following table provides the estimated future amortization of finite-lived intangible assets as of December 27, 2013 (in millions):
|
| | | |
2014 | $ | 5.8 |
|
2015 | 5.1 |
|
2016 | 4.6 |
|
2017 | 2.6 |
|
2018 | 2.1 |
|
Thereafter | 5.6 |
|
Total future amortization | $ | 25.8 |
|
Finite-lived intangible assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events and circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. We noted no such event or circumstance and accordingly no impairment loss was recognized during 2013, 2012, or 2011.
We also held indefinite lived trade name/trademarks of $5.7 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012. We test goodwill and indefinite lived intangible assets for impairment at least annually. We performed our annual goodwill impairment test as of the last day of our fiscal third quarter of 2013 and determined that the estimated fair value exceeded the carrying amount of goodwill for all our reporting units. Accordingly, no impairment loss was required to be recognized during 2013. We had no goodwill impairment losses during 2012 or 2011.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
| |
NOTE 8: | WORKERS’ COMPENSATION INSURANCE AND RESERVES |
We provide workers’ compensation insurance for our temporary and permanent employees. The majority of our current workers’ compensation insurance policies cover claims for a particular event above a $2.0 million deductible limit, on a “per occurrence” basis. This results in our being substantially self-insured.
In connection with the acquisition of MDT, we assumed certain workers' compensation insurance policies, which cover claims for the policy year ended February 13, 2013.
For workers’ compensation claims originating in Washington, North Dakota, Ohio, Wyoming, Canada, and Puerto Rico (our “monopolistic jurisdictions”), we pay workers’ compensation insurance premiums and obtain full coverage under government-administered programs (with the exception of our Labor Ready service line in the state of Ohio where we have a self-insured policy). Accordingly, because we are not the primary obligor, our financial statements do not reflect the liability for workers’ compensation claims in these monopolistic jurisdictions.
Our workers’ compensation reserve is established using estimates of the future cost of claims and related expenses that have been reported but not settled, as well as those that have been incurred but not reported. Our workers’ compensation reserve for claims below the deductible limit is discounted to its estimated net present value using discount rates based on average returns of “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments available during the year in which the liability was incurred. The weighted average rate was 2.1% and 2.4% at December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively.
The table below presents a reconciliation of the undiscounted workers’ compensation claims reserve to the discounted workers' compensation reserve for the periods presented as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27,
2013 | | December 28,
2012 |
Undiscounted workers’ compensation reserve | $ | 234.4 |
| | $ | 216.0 |
|
Less discount on workers' compensation reserve | 19.6 |
| | 20.4 |
|
Workers' compensation reserve, net of discount | 214.8 |
| | 195.6 |
|
Less current portion | 49.9 |
| | 44.7 |
|
Long-term portion | $ | 164.9 |
| | $ | 150.9 |
|
The table below presents the estimated future payout of our discounted workers' compensation claims reserve for the next five years and thereafter as of December 27, 2013 (in millions):
|
| | | |
2014 | $ | 49.9 |
|
2015 | 29.5 |
|
2016 | 18.6 |
|
2017 | 12.9 |
|
2018 | 9.9 |
|
2019 and thereafter | 59.9 |
|
Sub-total | 180.7 |
|
Excess claims reserve | 34.1 |
|
Total | $ | 214.8 |
|
Our workers’ compensation reserve includes estimated expenses related to claims above our self-insured limits (“excess claims”), and we record a corresponding receivable for the insurance coverage on excess claims based on the contractual policy agreements we have with insurance carriers. We discount this reserve and corresponding receivable to its estimated net present value using the discount rates based on average returns of “risk-free” U.S. Treasury instruments available during the year in which the liability was incurred. At December 27, 2013, the weighted average rate was 3.9%. The claim payments are made and the corresponding reimbursements from our insurance carriers are received over an estimated weighted average period of approximately 15.5 years. The discounted workers’ compensation reserve for excess claims and the corresponding receivable for the insurance on excess claims were $34.1 million and $27.1 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively.
Certain workers’ compensation insurance companies (“Troubled Insurance Companies”) with which we formerly did business are in liquidation and have failed to pay a number of excess claims to date. These excess claims have been presented to the state guaranty funds of the states in which the claims originated. Some of these excess claims have been rejected by the state guaranty funds due to statutory eligibility limitations. We have recorded a valuation allowance of $5.7 million and $5.6 million against all receivables from Troubled Insurance Companies for the excess claims that have primarily been rejected by the state guaranty as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. Total discounted receivables from insurance companies, net of the valuation allowance, were $28.4 million and $21.4 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively, and are included in Other assets, net in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Management evaluates the adequacy of the workers’ compensation reserves in conjunction with an independent quarterly actuarial assessment. Factors considered in establishing and adjusting these reserves include, among other things:
| |
• | changes in medical and time loss (“indemnity”) costs; |
| |
• | changes in mix between medical only and indemnity claims; |
| |
• | regulatory and legislative developments impacting benefits and settlement requirements; |
| |
• | type and location of work performed; |
| |
• | impact of safety initiatives; and |
| |
• | positive or adverse development of claims. |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
Workers’ compensation expense of $63.2 million, $52.3 million, and $51.2 million was recorded in Cost of services for 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Workers’ compensation expense consists primarily of: changes in self-insurance reserves net of changes in discount; monopolistic jurisdictions’ premiums; insurance premiums; and other miscellaneous expenses.
| |
NOTE 9: | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
Revolving credit facility
We have a credit agreement with Bank of America, N.A. and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC for a secured revolving credit facility of up to a maximum of $80.0 million (the “Revolving Credit Facility”). The Revolving Credit Facility expires in September 2016.
The maximum amount we can borrow under the Revolving Credit Facility is subject to certain borrowing limits. Specifically, we are limited to the sum of 85% of our eligible accounts receivable and the liquidation value of our Tacoma headquarters office building. The liquidation value is not to exceed $15.0 million, and is reduced quarterly by $0.4 million. As of December 27, 2013, the Tacoma headquarters office building liquidation value totaled $12.0 million. The borrowing limit is further reduced by the sum of a reserve in an amount equal to the payroll and payroll taxes for our temporary employees for one payroll cycle and other reserves, if deemed applicable. At December 27, 2013, $80.0 million was available under the Revolving Credit Facility, and $6.0 million was utilized by outstanding standby letters of credit, leaving $74.0 million available for additional borrowings. The letters of credit collateralize a portion of our workers' compensation obligation.
The Revolving Credit Facility requires that we maintain liquidity in excess of $12.0 million. Liquidity is defined as the amount we are entitled to borrow as advances under the Revolving Credit Facility plus the amount of cash, cash equivalents, and certain marketable securities held in accounts subject to a control agreement benefiting the lenders. We are required to satisfy a fixed charge coverage ratio in the event we do not meet that requirement. The amount we were entitled to borrow at December 27, 2013 was $74.0 million and the amount of cash, cash equivalents and certain marketable securities under control agreements was $124.5 million for a total of $198.5 million, which is well in excess of the liquidity requirement. We are currently in compliance with all covenants related to the Revolving Credit Facility.
Under the terms of the Revolving Credit Facility we pay a variable rate of interest on funds borrowed that is based on London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) or the Prime Rate, at our option, plus an applicable spread based on excess liquidity as set forth below:
|
| | | | |
Excess Liquidity | | Prime Rate Loans | | LIBOR Rate Loans |
Greater than $40 million | | 0.50% | | 1.50% |
Between $20 million and $40 million | | 0.75% | | 1.75% |
Less than $20 million | | 1.00% | | 2.00% |
A fee on borrowing availability of 0.25% is also applied against the unused portion of the Revolving Credit Facility. Letters of credit are priced at the margin in effect for LIBOR loans, plus a fronting fee of 0.125%.
Obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are secured by substantially all of our domestic personal property and our headquarters located in Tacoma, Washington.
Term Loan Agreement
On February 4, 2013, we entered into an unsecured Term Loan Agreement (the “Loan”) with Synovus Bank in the principal amount of $34.0 million. The Loan has a five year maturity with fixed monthly principal payments, which total $2.3 million annually based on a loan amortization term of fifteen years. Interest accrues at the one-month LIBOR index rate plus an applicable spread of 1.50%, which is paid in addition to the principal payments. At our discretion, we may elect to extend the term of the Loan by five consecutive one-year extensions. At December 27, 2013, the interest rate for the term loan was 1.7%.
At December 27, 2013, the remaining balance of the Loan was $32.0 million, of which, $2.3 million is short-term and is included in Other current liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The long term portion of $29.7 million is reported as Note payable on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The loan has variable rate interest and approximates fair value as of December 27, 2013.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
Scheduled principal payments for debt for the next five years are as follows (in millions): |
| | | |
2014 | $ | 2.3 |
|
2015 | 2.3 |
|
2016 | 2.3 |
|
2017 | 2.3 |
|
2018 | 22.8 |
|
Total principal payments | $ | 32.0 |
|
Our obligations under the Loan may be accelerated upon the occurrence of an event of default under the Loan, which includes customary events of default, as well as cross-defaults related to indebtedness under our Revolving Credit Facility, and other Loan specific defaults. The Loan contains customary negative covenants applicable to the Company and its subsidiaries such as indebtedness, certain dispositions of property, the imposition of restrictions on payments under the Loan, and other Loan specific covenants. We are in compliance with all covenants related to the Loan as of December 27, 2013.
Workers’ compensation commitments
Our insurance carriers and certain state workers’ compensation programs require us to collateralize a portion of our workers’ compensation obligation, for which they become responsible should we become insolvent. The collateral typically takes the form of cash and cash equivalents, highly rated investment grade debt securities, letters of credit and/or surety bonds. On a regular basis these entities assess the amount of collateral they will require from us relative to our workers' compensation obligation. The majority of our collateral obligations are held in the Trust at the Bank of New York Mellon.
We have provided our insurance carriers and certain states with commitments in the form and amounts listed below (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27,
2013 | | December 28,
2012 |
Cash collateral held by insurance carriers | $ | 23.7 |
| | $ | 21.5 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents held in Trust (1) | 31.5 |
| | 14.8 |
|
Investments held in Trust | 86.7 |
| | 91.2 |
|
Letters of credit (2) | 7.9 |
| | 9.0 |
|
Surety bonds (3) | 16.1 |
| | 16.2 |
|
Total collateral commitments | $ | 165.9 |
| | $ | 152.7 |
|
| |
(1) | Included in this amount is $0.8 million and $0.9 million of accrued interest at December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. |
| |
(2) | We have agreements with certain financial institutions to issue letters of credit as collateral. We had $1.9 million and $1.8 million of restricted cash collateralizing our letters of credit at December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. |
| |
(3) | Our surety bonds are issued by independent insurance companies on our behalf and bear annual fees based on a percentage of the bond, which is determined by each independent surety carrier. These fees do not exceed 2.0% of the bond amount, subject to a minimum charge. The terms of these bonds are subject to review and renewal every one to four years and most bonds can be canceled by the sureties with as little as 60 days notice. |
Capital leases
We had property held under non-cancelable capital leases reported in Property and equipment, net on the Consolidated Balance Sheets totaling $0.1 million, net of accumulated depreciation at December 28, 2012. At December 27, 2013 we held no capital leases. Our capital lease obligations were reported in Other current liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
Operating leases
We have contractual commitments in the form of operating leases related to branch offices and equipment. Future non-cancelable minimum lease payments under our operating lease commitments as of December 27, 2013 are as follows for each of the next five years and thereafter (in millions):
|
| | | |
2014 | $ | 1.8 |
|
2015 | 1.0 |
|
2016 | 0.5 |
|
2017 | 0.2 |
|
2018 | 0.1 |
|
Total future non-cancelable minimum lease payments | $ | 3.6 |
|
The majority of operating leases pertaining to our branch offices provide for renewal options ranging from three to five years. Operating leases are generally renewed in the normal course of business, and most of the options are negotiated at the time of renewal. However, for the majority of our leases, both parties to the lease have the right to cancel the lease with 90 days notice. Accordingly, we have not included the leases with 90 day cancellation provisions in our disclosure of future minimum lease payments.
Total branch office rent expense for 2013, 2012, and 2011 was $22.5 million, $22.0 million and $22.1 million, respectively.
Purchase Obligations
Purchase obligations include agreements to purchase goods and services in the ordinary course of business that are enforceable, legally binding and specify all significant terms. Purchase obligations do not include agreements that are cancelable without significant penalty. We had $16.8 million of purchase obligations as of December 27, 2013, of which $8.9 million are expected to be paid in 2014.
Legal contingencies and developments
We are involved in various proceedings arising in the normal course of conducting business. We believe the amounts provided in our financial statements are adequate in consideration of the probable and estimable liabilities. The resolution of those proceedings is not expected to have a material effect on our results of operations or financial condition.
| |
NOTE 10: | STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY |
Common Stock
In July 2011, our Board of Directors approved a program to repurchase $75 million of our outstanding common stock. As of December 27, 2013, $35.2 million remained available for repurchase of common stock under the current authorization, which has no expiration date.
During 2013, we did not repurchase or retire any shares of our common stock under our authorized stock repurchase program. During 2012, we repurchased and retired 0.3 million shares of our common stock for a total amount of $4.4 million, including commissions.
Purchases of our common stock are not displayed separately as treasury stock on the Consolidated Balance Sheets in accordance with the Washington Business Corporation Act, which requires the retirement of purchased shares. As a result, shares of our common stock that we purchase are retired immediately. It is our policy to first record these purchases as a reduction to our common stock account. Once the common stock account has been reduced to a nominal balance, remaining purchases are recorded as a reduction to retained earnings.
Preferred Stock
We have authorized 20 million shares of blank check preferred stock. The blank check preferred stock is issuable in one or more series, each with such designations, preferences, rights, qualifications, limitations and restrictions as our Board of Directors may determine and set forth in supplemental resolutions at the time of issuance, without further shareholder action.
The initial series of blank check preferred stock authorized by the Board of Directors was designated as Series A Preferred Stock. We had no outstanding shares of preferred stock in any of the years presented.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
NOTE 11:STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
We record stock-based compensation expense for restricted and unrestricted stock awards, performance share units, stock options, and shares purchased under an employee stock purchase plan.
Stock-based compensation expense was as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Restricted and unrestricted stock and performance share units | $ | 8.1 |
| | $ | 7.5 |
| | $ | 6.7 |
|
Stock options | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | 0.4 |
|
Employee stock purchase plan | 0.3 |
| | 0.3 |
| | 0.3 |
|
Total stock-based compensation | $ | 8.4 |
| | $ | 7.9 |
| | $ | 7.4 |
|
| | |
|
| | |
Total related tax benefit recognized | $ | 2.9 |
| | $ | 2.9 |
| | $ | 2.8 |
|
Our 2005 Long-Term Equity Incentive Plan, as amended and restated effective May 2013 ("Incentive Plan"), provides for the issuance or delivery of up to 7.95 million shares of our common stock over the full term of the Incentive Plan.
No capitalized stock-based compensation was included in Property and equipment, net on the Consolidated Balance Sheets for 2013, 2012 or 2011.
Restricted and unrestricted stock and performance share units
Under the Incentive Plan, restricted stock is granted to executive officers and key employees and vests annually over three or four years. Unrestricted stock granted to our directors vests immediately. Restricted and unrestricted stock-based compensation expense is calculated based on the grant-date market value. We recognize compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period, net of estimated forfeitures.
Performance share units have been granted to executive officers and certain key employees since 2010. Vesting of the performance share units is contingent upon the achievement of revenue and/or profitability growth goals at the end of each three year performance period. Each performance share unit is equivalent to one share of common stock. Compensation expense is calculated based on the grant-date market value of our stock and is recognized ratably over the performance period for the performance share units which are expected to vest. Our estimate of the performance units expected to vest is reviewed and adjusted as appropriate each quarter.
Restricted and unrestricted stock and performance share units activity for the year ended December 27, 2013 was as follows (shares in thousands):
|
| | | | | | |
| Shares | | Weighted- average grant-date price |
Non-vested at beginning of period | 1,435 |
| | $ | 15.23 |
|
Granted | 643 |
| | $ | 19.00 |
|
Vested | (437 | ) | | $ | 15.25 |
|
Forfeited | (97 | ) | | $ | 17.45 |
|
Non-vested at the end of the period | 1,544 |
| | $ | 16.66 |
|
The weighted average grant-date price of restricted and unrestricted stock and performance share units granted during the years 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $19.00, $16.72, and $14.72, respectively. As of December 27, 2013, total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to non-vested restricted stock was approximately $8.3 million, of which $7.4 million is estimated to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.7 years through 2017. As of December 27, 2013, total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to performance share units, assuming achievement of maximum financial goals, was approximately $8.1 million, of which $2.8 million is currently estimated to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.6 years through 2015. The total fair value of restricted shares vesting during 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $4.8 million, $5.3 million and $5.2 million, respectively.
Stock options
Our Incentive Plan provides for both nonqualified stock options and incentive stock options (collectively, “stock options”) for directors, officers, and certain employees. We issue new shares of common stock upon exercise of stock options. All of our stock options are vested and expire if not exercised within seven years from the date of grant. The maximum contractual term for our outstanding option awards is ten years.
There were no stock options granted during fiscal 2013, 2012 or 2011.
Stock option activity was as follows (shares in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shares | | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in millions) |
Outstanding, December 28, 2012 | 639 |
| | $ | 16.91 |
| | | | |
Exercised | (454 | ) | | $ | 16.12 |
| | | | |
Expired/Forfeited | (111 | ) | | $ | 21.24 |
| | | | |
Outstanding, December 27, 2013 | 74 |
| | $ | 14.99 |
| | 1.65 | | $ | 0.8 |
|
Exercisable, December 27, 2013 | 74 |
| | $ | 14.99 |
| | 1.65 | | $ | 0.8 |
|
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above is the amount by which the market value of the underlying stock exceeded the exercise price of outstanding options, before applicable income taxes and represents the amount optionees would have realized if all in-the-money options had been exercised on the last business day of the period indicated. The closing per share market value of the Company’s stock on December 27, 2013 was $25.92.
Total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to non-vested stock options was de minimis as of December 27, 2013. The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $3.0 million and $1.9 million, in 2013 and 2012, respectively, and was de minimis in 2011, determined as of the date of exercise.
Cash received from option exercises, net of tax withholdings, during 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $7.3 million, $2.5 million and $0.1 million, respectively. The actual tax benefit realized for the deduction from option exercises was $1.0 million and $0.6 million in 2013 and 2012, respectively, and was de minimis for 2011.
Employee stock purchase plan
Our Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) reserves for purchase 1.0 million shares of common stock. The plan allows eligible employees to contribute up to 10% of their earnings toward the monthly purchase of the Company's common stock. The employee's purchase price is the lesser of 85% of the fair market value of shares on either the first day or the last day of each month. We consider our ESPP to be a component of our stock-based compensation and accordingly we recognize compensation expense over the requisite service period for stock purchases made under the plan. The requisite service period begins on the enrollment date and ends on the purchase date, the duration of which is one month.
The following table summarizes transactions under our ESPP from fiscal year 2011 through 2013 (shares in thousands):
|
| | | | | | |
| Shares | | Average Price Per
Share |
Issued during fiscal year 2013 | 69 |
| | $ | 17.10 |
|
Issued during fiscal year 2012 | 95 |
| | $ | 12.41 |
|
Issued during fiscal year 2011 | 83 |
| | $ | 11.95 |
|
The provision for income taxes is comprised of the following (in millions):
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Current taxes: | | | | | |
Federal | $ | 14.2 |
| | $ | 14.9 |
| | $ | 16.3 |
|
State | 5.1 |
| | 2.7 |
| | 2.9 |
|
Foreign | 0.5 |
| | 0.3 |
| | 0.4 |
|
Total current taxes | 19.8 |
| | 17.9 |
| | 19.6 |
|
Deferred taxes: | | | | | |
Federal | (2.8 | ) | | 2.7 |
| | (1.3 | ) |
State | (1.0 | ) | | 0.4 |
| | 0.1 |
|
Foreign | — |
| | — |
| | 0.1 |
|
Total deferred taxes | (3.8 | ) | | 3.1 |
| | (1.1 | ) |
Provision for income taxes | $ | 16.0 |
| | $ | 21.0 |
| | $ | 18.5 |
|
The items accounting for the difference between income taxes computed at the statutory federal income tax rate and income taxes reported in the Consolidated Statements of Operations & Comprehensive Income are as follows (in millions except percentages):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | % | | 2012 | | % | | 2011 | | % |
Income tax expense based on statutory rate | $ | 21.3 |
| | 35.0 | % | | $ | 19.1 |
| | 35.0 | % | | $ | 17.2 |
| | 35.0 | % |
Increase (decrease) resulting from: | | | | | | | | | | | |
State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 2.5 |
| | 4.2 | % | | 1.8 |
| | 3.3 | % | | 1.9 |
| | 3.9 | % |
Tax credits, net | (10.8 | ) | | (17.7 | )% | | (1.9 | ) | | (3.5 | )% | | (3.5 | ) | | (7.2 | )% |
Nondeductible/nontaxable items | 2.1 |
| | 3.5 | % | | 2.3 |
| | 4.2 | % | | 2.9 |
| | 5.8 | % |
Other, net | 0.9 |
| | 1.3 | % | | (0.3 | ) | | (0.6 | )% | | — |
| | 0.1 | % |
Total taxes on income | $ | 16.0 |
| | 26.3 | % | | $ | 21.0 |
| | 38.4 | % | | $ | 18.5 |
| | 37.6 | % |
The primary difference between the statutory federal income tax rate of 35.0% and our annual effective income tax rate of 26.3%, excluding the prior year WOTC benefits, is from estimated current year WOTC, state income taxes, and certain non-deductible expenses.
Our effective tax rate on earnings for the year ended December 27, 2013, was 26.3% compared to 38.4% for the same period in 2012. The decrease in the effective tax rate is due primarily to the federal Work Opportunity Tax Credit (“WOTC”). The effective tax rate for 2012 excluded benefits of WOTC because it had largely expired at the end of 2011. The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (the “Act”) was signed into law on January 2, 2013, and retroactively restored the WOTC for 2012 and extended it through 2013. This tax credit is designed to encourage employers to hire workers from certain targeted groups with higher than average unemployment rates. Because a change in the law is accounted for in the period of enactment, the retroactive effect of the Act on our U.S. federal taxes for 2012 was recognized in the year ended December 27, 2013. The effective tax rate was also favorably impacted by the estimated increase to our WOTC benefits from the IRS extension of the 2012 WOTC certification request deadline to April 29, 2013, and by receipt of additional WOTC certification approvals related to years prior to 2012.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
The components of deferred tax assets and liabilities were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| December 27, 2013 | | December 28, 2012 |
Deferred tax assets: | | | |
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 2.2 |
| | $ | 2.0 |
|
Workers’ compensation claims reserve | 10.4 |
| | 10.1 |
|
Accounts payable and other accrued expenses | 2.2 |
| | 2.4 |
|
Net operating loss and tax credits carry-forwards | 1.1 |
| | 0.6 |
|
Accrued wages and benefits | 6.8 |
| | 5.9 |
|
Deferred compensation | 2.2 |
| | 1.5 |
|
Other | 1.0 |
| | 0.5 |
|
Total | 25.9 |
| | 23.0 |
|
Valuation allowance | (0.8 | ) | | (0.6 | ) |
Total deferred tax asset, net of valuation allowance | 25.1 |
| | 22.4 |
|
Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
Prepaid expenses, deposits and other current assets | (1.7 | ) | | (1.6 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | (10.4 | ) | | (11.9 | ) |
Other | (1.2 | ) | | (0.9 | ) |
Total deferred tax liabilities | (13.3 | ) | | (14.4 | ) |
Net deferred tax asset, end of year | 11.8 |
| | 8.0 |
|
Net deferred tax asset, current | 7.6 |
| | 5.4 |
|
Net deferred tax asset, non-current | $ | 4.2 |
| | $ | 2.6 |
|
At December 27, 2013, Spartan Staffing Puerto Rico, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of TrueBlue, Inc., had net operating loss carry-forwards of approximately $2.7 million expiring in 2015 through 2022. Additionally, Labor Ready Southwest, Inc. and its affiliates, wholly-owned subsidiaries of TrueBlue, Inc., had California enterprise zone tax credit carry-forwards of approximately $1.0 million expiring in 2023. Valuation allowances have been established against our carry-forward tax benefits based on our history.
Deferred taxes related to our foreign currency translation were de minimis for 2013, 2012 and 2011.
As of December 27, 2013, our liability for unrecognized tax benefits was $2.0 million, if recognized, $1.3 million would impact our effective tax rate. We do not believe the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits will significantly increase or decrease within 12 months of the year ended December 27, 2013. This liability is recorded in Other non-current liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. In general, the tax years 2010 through 2012 remain open to examination by the major taxing jurisdictions where we conduct business.
The following table summarizes the activity related to our unrecognized tax benefits (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Balance, beginning of fiscal year | $ | 1.9 |
| | $ | 1.7 |
| | $ | 1.6 |
|
Increases for tax positions related to the current year | 0.4 |
| | 0.5 |
| | 0.3 |
|
Reductions due to lapsed statute of limitations | (0.3 | ) | | (0.3 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
Balance, end of fiscal year | $ | 2.0 |
| | $ | 1.9 |
| | $ | 1.7 |
|
We recognize interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits within Income tax expense on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations & Comprehensive Income. Accrued interest and penalties are included within Other long-term liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Related to the unrecognized tax benefits noted above, we accrued a de minimis amount for interest and penalties during 2013 and in total, as of December 27, 2013, have recognized a liability for penalties of$0.2 million and interest of $0.7 million.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
NOTE 13:DEFINED CONTRIBUTION PLANS
We offer both qualified and non-qualified defined contribution plans to eligible employees. Participating employees may elect to defer and contribute a portion of their eligible compensation. The plans offer discretionary matching contributions. The liability for the nonqualified plan was $6.6 million and $4.2 million as of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, respectively. The current and non-current portion of the deferred compensation liability is included in Other current liabilities and Other long-term liabilities, respectively, on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, and is largely offset by restricted investments recorded in Restricted cash and investments on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The expense for our qualified and nonqualified deferred compensation plans, including our discretionary matching contributions, totaled $1.4 million, $1.2 million, and $1.1 million for 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively, and is recorded in Selling, general and administrative expenses on the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income.
| |
NOTE 14. | NET INCOME PER SHARE |
Adjusted net income and diluted common shares were calculated as follows (in millions, except per share amounts):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Net income | $ | 44.9 |
| | $ | 33.6 |
| | $ | 30.8 |
|
| | | | | |
Weighted average number of common shares used in basic net income per common share | 40.2 |
| | 39.5 |
| | 42.0 |
|
Dilutive effect of outstanding stock options and non-vested restricted stock | 0.3 |
| | 0.4 |
| | 0.3 |
|
Weighted average number of common shares used in diluted net income per common share | 40.5 |
| | 39.9 |
| | 42.3 |
|
Net income per common share: | | | | | |
Basic | $ | 1.12 |
| | $ | 0.85 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
|
Diluted | $ | 1.11 |
| | $ | 0.84 |
| | $ | 0.73 |
|
| | | | | |
Anti-dilutive shares | 0.1 |
| | 0.7 |
| | 1.0 |
|
Basic net income per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares and potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential common shares include the dilutive effects of outstanding options, non-vested restricted stock, and performance share units, except where their inclusion would be anti-dilutive.
Anti-dilutive shares include unvested restricted stock, performance share units and in-the-money options for which the sum of the assumed proceeds, including unrecognized compensation expense, exceeds the average stock price during the periods presented. Anti-dilutive shares associated with our stock options relate to those stock options with an exercise price higher than the average market value of our stock during the periods presented.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
| |
NOTE 15. | OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
Other comprehensive income (loss) is reflected as a net increase (decrease) to shareholders’ equity. Changes in the balances of each component of accumulated comprehensive income (loss) during the year ended December 27, 2013 were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | | Unrealized loss on marketable securities (1) | | Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax (2) |
Balance as of December 28, 2012 | $ | 2.8 |
| | $ | 0.0 |
| | $ | 2.8 |
|
Current-period other comprehensive loss | (0.7 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (0.8 | ) |
Balance as of December 27, 2013 | $ | 2.1 |
| | $ | (0.1 | ) | | $ | 2.0 |
|
| |
(1) | Consists of deferred compensation plan accounts, which are comprised of mutual funds, and available-for-sale securities, which are comprised of certificates of deposits. |
| |
(2) | The tax impact of the components of other comprehensive income (loss) was immaterial. |
| |
NOTE 16: | SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION |
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Cash paid during the period for: | | | | | |
Interest | $ | 1.1 |
| | $ | 0.7 |
| | $ | 0.8 |
|
Income taxes | $ | 15.6 |
| | $ | 21.3 |
| | $ | 16.1 |
|
As of December 27, 2013 and December 28, 2012, we had acquired $0.5 million and $1.6 million, respectively, of property, plant and equipment on account that was not yet paid. These are considered non-cash investing items.
| |
NOTE 17: | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS |
We evaluated events and transactions occurring after the balance sheet date through the date the financial statements were issued, and noted no other events that were subject to recognition or disclosure.
SELECTED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED)
IN THOUSANDS (EXCEPT PER SHARE DATA)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth |
2013 | | | | | | | |
Revenue from services | $ | 346,498 |
| | $ | 422,310 |
| | $ | 451,169 |
| | $ | 448,952 |
|
Cost of services | 259,859 |
| | 310,437 |
| | 327,641 |
| | 328,689 |
|
Gross profit | 86,639 |
| | 111,873 |
| | 123,528 |
| | 120,263 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 88,432 |
| | 89,339 |
| | 90,767 |
| | 93,710 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 5,159 |
| | 5,203 |
| | 4,771 |
| | 5,339 |
|
Income (loss) from operations | (6,952 | ) | | 17,331 |
| | 27,990 |
| | 21,214 |
|
Interest expense | (233 | ) | | (336 | ) | | (350 | ) | | (329 | ) |
Interest and other income | 710 |
| | 611 |
| | 766 |
| | 515 |
|
Interest and other income, net | 477 |
| | 275 |
| | 416 |
| | 186 |
|
Income (loss) before tax expense | (6,475 | ) | | 17,606 |
| | 28,406 |
| | 21,400 |
|
Income tax expense (benefit) | (5,399 | ) | | 5,069 |
| | 9,454 |
| | 6,889 |
|
Net income (loss) | $ | (1,076 | ) | | $ | 12,537 |
| | $ | 18,952 |
| | $ | 14,511 |
|
Net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | |
Basic | $ | (0.03 | ) | | $ | 0.31 |
| | $ | 0.47 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
|
Diluted | $ | (0.03 | ) | | $ | 0.31 |
| | $ | 0.47 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
|
2012 | | | | | | | |
Revenue from services | $ | 311,187 |
| | $ | 354,261 |
| | $ | 379,467 |
| | $ | 344,615 |
|
Cost of services | 231,952 |
| | 260,725 |
| | 274,237 |
| | 250,231 |
|
Gross profit | 79,235 |
| | 93,536 |
| | 105,230 |
| | 94,384 |
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 72,082 |
| | 71,526 |
| | 77,634 |
| | 79,217 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 4,768 |
| | 4,729 |
| | 4,660 |
| | 4,733 |
|
Income from operations | 2,385 |
| | 17,281 |
| | 22,936 |
| | 10,434 |
|
Interest expense | (391 | ) | | (244 | ) | | (266 | ) | | (230 | ) |
Interest and other income | 655 |
| | 656 |
| | 675 |
| | 714 |
|
Interest and other income, net | 264 |
| | 412 |
| | 409 |
| | 484 |
|
Income before tax expense | 2,649 |
| | 17,693 |
| | 23,345 |
| | 10,918 |
|
Income tax expense | 1,119 |
| | 7,356 |
| | 8,998 |
| | 3,503 |
|
Net income | $ | 1,530 |
| | $ | 10,337 |
| | $ | 14,347 |
| | $ | 7,415 |
|
Net income per common share: | | | | | | | |
Basic | $ | 0.04 |
| | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
| | $ | 0.19 |
|
Diluted | $ | 0.04 |
| | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
| | $ | 0.19 |
|
| |
Item 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| |
Item 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company, we have evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as required by Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(e) as of the end of the period
covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that these disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. Internal control over financial reporting is a process to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of our financial reporting for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Internal control over financial reporting includes maintaining records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect our transactions; providing reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary for preparation of our financial statements; providing reasonable assurance that receipts and expenditures of Company assets are made in accordance with management authorization; and providing reasonable assurance that unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of Company assets that could have a material effect on our financial statements would be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements.
Management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, management concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 27, 2013. There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 27, 2013 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting. The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 27, 2013 has been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report, which is included herein.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of TrueBlue, Inc.
Tacoma, Washington
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of TrueBlue, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 27, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 27, 2013, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedules as of and for the fiscal year ended December 27, 2013 of the Company and our report dated February 20, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedules.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Seattle, Washington
February 20, 2014
| |
Item 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
| |
Item 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Information regarding our directors and nominees for directorship is presented under the heading “Election of Directors” in our definitive proxy statement for use in connection with the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (the “Proxy Statement”) to be filed within 120 days after our fiscal year ended December 27, 2013, and is incorporated herein by this reference thereto. Information concerning our executive officers is set forth under the heading “Executive Officers” in our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference thereto. Information regarding compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, our code of business conduct and ethics and certain information related to the Company’s Audit Committee and Governance Committee is set forth under the heading “Corporate Governance” in our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference thereto.
| |
Item 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
Information regarding the compensation of our directors and executive officers and certain information related to the Company’s Compensation Committee is set forth under the headings “Executive Compensation Tables,” “Director Compensation,” “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Compensation Committee Report” and “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” in our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by this reference thereto.
| |
Item 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDERS |
Information with respect to security ownership of certain beneficial owners and management is set forth under the headings “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by this reference thereto.
| |
Item 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
Information regarding certain relationships and related transactions and director independence is presented under the heading “Corporate Governance” in our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by this reference thereto.
| |
Item 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICE |
Information concerning principal accounting fees and services is presented under the heading “Fees Paid to Independent Public Accountant for Fiscal Years 2012 and 2013” in our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by this reference thereto.
| |
Item 15. | EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
| |
a) | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
| |
1. | Financial Statements can be found under Item 8 of Part II of this Form 10-K. |
| |
2. | Financial Statement Schedules can be found on Page 65 of this Form 10-K. |
| |
3. | The Exhibit Index is found on Page 66 of this Form 10-K. |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | | | |
| | TrueBlue, Inc. | | |
| | | | |
| | /s/ Steven C. Cooper | 2/20/2014 | |
| | Signature | Date | |
| | By: Steven C. Cooper, Director, Chief Executive Officer and President | | |
| | | | |
| | /s/ Derrek L. Gafford | 2/20/2014 | |
| | Signature | Date | |
| | By: Derrek L. Gafford, Chief Financial Officer and Executive Vice President | | |
| | | | |
| | /s/ Norman H. Frey | 2/20/2014 | |
| | Signature | Date | |
| | By: Norman H. Frey, Chief Accounting Officer and
Vice President | | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
/s/ Steven C. Cooper | | 2/20/2014 | | | | /s/ Joseph P. Sambataro, Jr. | | 2/20/2014 | | |
Signature | | Date | | | | Signature | | Date | | |
Steven C. Cooper, Director, Chief Executive Officer and President | | | | | | Joseph P. Sambataro, Jr., Chairman of the Board | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
/s/ Craig Tall | | 2/20/2014 | | | | /s/ Jeffrey B. Sakaguchi | | 2/20/2014 | | |
Signature | | Date | | | | Signature | | Date | | |
Craig Tall, Director | | | | | | Jeffrey B. Sakaguchi, Director | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
/s/ Thomas E. McChesney | | 2/20/2014 | | | | /s/ William W. Steele | | 2/20/2014 | | |
Signature | | Date | | | | Signature | | Date | | |
Thomas E. McChesney, Director | | | | | | William W. Steele, Director | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
/s/ Gates McKibbin | | 2/20/2014 | | | | /s/ Bonnie W. Soodik | | 2/20/2014 | | |
Signature | | Date | | | | Signature | | Date | | |
Gates McKibbin, Director | | | | | | Bonnie W. Soodik, Director | | | | |
FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
Schedule II, Valuation and Qualifying Accounts (in millions)
Allowance for doubtful accounts activity was as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 5.0 |
| | $ | 5.8 |
| | $ | 6.4 |
|
Charged to expense | 12.1 |
| | 7.0 |
| | 6.6 |
|
Write-offs | (11.4 | ) | | (7.8 | ) | | (7.2 | ) |
Balance, end of year | $ | 5.7 |
| | $ | 5.0 |
| | $ | 5.8 |
|
Insurance receivable valuation allowance activity was as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 5.6 |
| | $ | 7.3 |
| | $ | 7.6 |
|
Charged to expense | 0.1 |
| | (1.7 | ) | | (0.3 | ) |
Balance, end of year | $ | 5.7 |
| | $ | 5.6 |
| | $ | 7.3 |
|
Income tax valuation allowance additions (reductions) were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 0.6 |
| | $ | 0.5 |
| | $ | 0.7 |
|
Charged to expense | 0.2 |
| | 0.1 |
| | (0.2 | ) |
Balance, end of year | $ | 0.8 |
| | $ | 0.6 |
| | $ | 0.5 |
|
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | Incorporated by Reference |
Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description | Form | | File No. | | Date of First Filing |
| | | | | | | |
3.1 | | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation | 8-K | | 001-14543 | | 6/16/2009 |
| | | | | | | |
3.2 | | Amended and Restated Company Bylaws | 8-K | | 001-14543 | | 9/17/2008 |
| | | | | | | |
10.1 | | 1996 Employee Stock Option and Incentive Plan | DEF 14A | | 000-23828 | | 7/23/1996 |
| | | | | | | |
10.2 | | Assumption and Novation Agreement among TrueBlue, Inc. and Lumbermen's Mutual Casualty Company, American Motorist Insurance Company, American Protection Insurance Company and American Manufacturers Mutual Insurance Company and National Union Fire Insurance Company of Pittsburgh, PA, dated December 29, 2004 | 10-K | | 001-14543 | | 3/11/2005 |
| | | | | | | |
10.3 | | Indemnification Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and National Union Fire Insurance Company of Pittsburgh, PA dated December 29, 2004 | 10-K | | 001-14543 | | 3/11/2005 |
| | | | | | | |
10.4 | | Executive Employment Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and James E. Defebaugh, dated August 3, 2005 | 8-K | | 001-14543 | | 8/9/2005 |
| | | | | | | |
10.5 | | First Amendment to the Executive Employment Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and James E. Defebaugh, dated December 31, 2006 | 10-Q | | 001-14543 | | 5/4/2007 |
| | | | | | | |
10.6 | | Executive Employment Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Derrek Gafford, dated December 31, 2006 | 10-Q | | 001-14543 | | 5/4/2007 |
| | | | | | | |
10.7 | | Executive Employment Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Wayne Larkin, dated December 31, 2006 | 10-Q | | 001-14543 | | 5/4/2007 |
| | | | | | | |
10.8 | | Form Executive Non-Competition Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Steven Cooper, Jim Defebaugh, Derrek Gafford, Wayne Larkin, and Kimberly Cannon | 10-Q | | 001-14543 | | 5/4/2007 |
| | | | | | | |
10.9 | | Form Executive Indemnification Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Steven Cooper, Jim Defebaugh, Derrek Gafford, and Wayne Larkin, and Kimberly Cannon | 10-Q | | 001-14543 | | 5/4/2007 |
| | | | | | | |
10.10 | | Form Executive Change in Control Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Steven Cooper, Jim Defebaugh, Derrek Gafford, Wayne Larkin, and Kimberly Cannon | 10-Q | | 001-14543 | | 5/4/2007 |
10.11 | | Amended and Restated Executive Employment Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Steven C. Cooper, dated November 16, 2009 | 8-K | | 001-14543 | | 11/19/2009 |
| | | | | | | |
10.12 | | Amended and Restated Non-Competition Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Steven Cooper, dated November 16, 2009 | 8-K | | 001-14543 | | 11/19/2009 |
| | | | | | | |
10.13 | | Equity Retainer And Deferred Compensation Plan For Non- Employee Directors, effective January 1, 2010 | S-8 | | 333-164614 | | 2/1/2010 |
| | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | Incorporated by Reference |
Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description | Form | | File No. | | Date of First Filing |
| | | | | | | |
10.14 | | 2010 Employee Stock Purchase Plan | S-8 | | 333-167770 | | 6/25/2010 |
| | | | | | | |
10.15 | | Executive Employment Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Kimberly Cannon, dated November 8, 2010 | 10-K | | 001-14543 | | 2/2/2012 |
| | | | | | | |
10.16 | | Amended and Restated Credit Agreement between TrueBlue, Inc. and Bank of America and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, dated September 30, 2011 | 8-K | | 001-14543 | | 10/4/2011 |
| | | | | | | |
10.17 | | TrueBlue, Inc. Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan | 10-K | | 001-14543 | | 2/22/2012 |
| | | | | | | |
10.18 | | Asset Purchase Agreement among MDT Personnel, LLC, MDT Personnel Contracts, LLC, MDT Staffing, LLC, Disaster Recovery Support, LLC, Michael D. Traina, TrueBlue, Inc., and Labor Ready Holdings, Inc. dated as of February 4, 2013 | 10-K | | 001-14543 | | 2/21/2013 |
| | | | | | | |
10.19 | | Term Loan Agreement by and among TrueBlue, Inc., The Lenders That Signatories hereto, and Synovus Bank as of February 4, 2013 | 10-K | | 001-14543 | | 2/21/2013 |
| | | | | | | |
10.20 | | Amended and Restated 2005 Long-Term Equity Incentive Plan | S-8 | | 333-190220 | | 7/29/2013 |
| | | | | | | |
21.1* | | Subsidiaries of TrueBlue, Inc. | — | | — | | — |
| | | | | | | |
23.1* | | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP - Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | — | | — | | — |
| | | | | | | |
31.1* | | Certification of Steven C. Cooper, Chief Executive Officer of TrueBlue, Inc., Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a), as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | — | | — | | — |
| | | | | | | |
31.2* | | Certification of Derrek L. Gafford, Chief Financial Officer of TrueBlue, Inc., Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a), as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | — | | — | | — |
| | | | | | | |
32.1* | | Certification of Steven C. Cooper, Chief Executive Officer of TrueBlue, Inc. and Derrek L. Gafford, Chief Financial Officer of TrueBlue, Inc., Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | — | | — | | — |
| | | | | | | |
101** | | The following financial information from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 27, 2013, formatted in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations & Comprehensive Income, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Shareholders' Equity, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (v) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, and (vi) Schedule II, Valuation and Qualifying Accounts | — | | — | | — |
Copies of Exhibits may be obtained upon request directed to Mr. James Defebaugh or Mr. Derrek Gafford, TrueBlue, Inc., PO Box 2910, Tacoma, Washington, 98401 and many are available at the SEC’s website found at www.sec.gov.